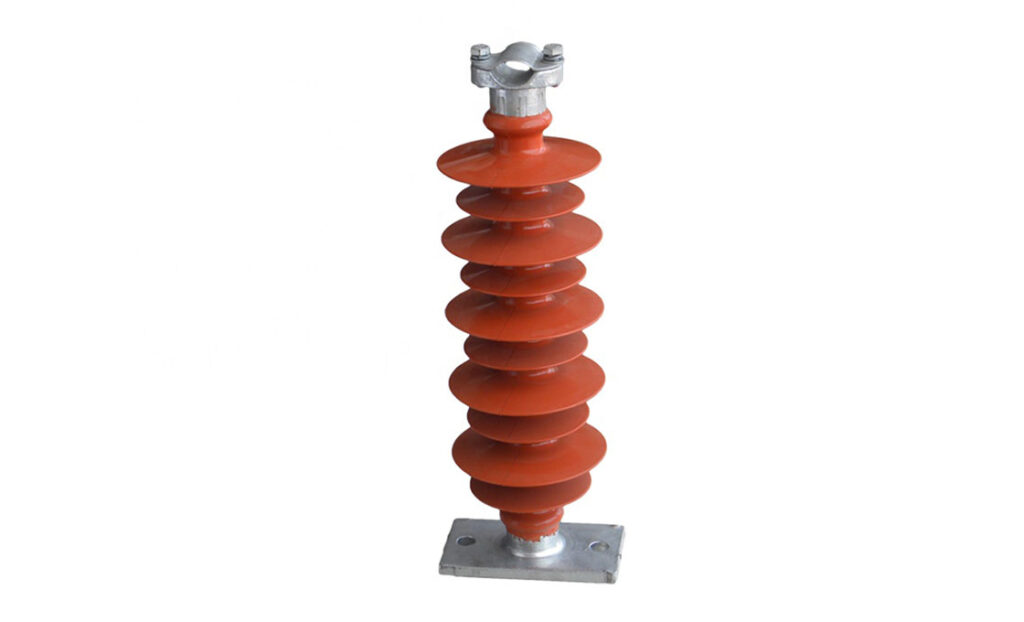

A post insulator is a type of insulator used in high voltage transmission lines and electrical systems. It helps to support and insulate the conductors from the support structures. This helps to prevent current leakage to ensure safe transmission of electricity. Post insulators are from porcelain, glass or composite materials. They also offer mechanical support and withstand mechanical stresses from wind and ice. Post insulators come in various designs including solid core, hollow core and composite insulators. The design depends on factors such as voltage rating, environmental conditions and mechanical requirements. They work well in voltage ranging from low voltage to extra-high voltage transmission lines. Common types of post insulators include line post insulators and station post insulators. Using post insulators help to provide electrical insulation and mechanical support to conductors.
Components of a post insulator
Post insulators consist of several components that contribute to the effectiveness of the transmission lines. Their designs and components of the post insulator vary depending on voltage rating and application requirements. They work together to provide electrical insulation, mechanical support and safe operation. The following are the common components of a post insulator.
- Insulating core – this is the central part of the post insulator that provides electrical insulation. It is from a non-conductive material like porcelain, glass or polymer. It also supports the conductive fittings or terminals.
- Shed – this is the outer covering of the insulator core which helps to increase the creepage distance. It has designs to shed water and reduce the risk of flashovers.
- Conductive fittings – post insulators have conductive fittings at each end which are from metal. They ease mounting onto the supporting structure and connection to conductors. The fittings from galvanized steel or aluminum provide electrical connectivity and mechanical strength.
- Cement – the core of the post insulator may need cement to enhance mechanical strength and weather resistance. This helps to protect the insulator from environmental factors like moisture and UV radiation.
- Mounting components – the insulators need hardware and mounting components to secure them to the supporting structure. They include metal flanges, clamps, bolts among others. These components allow proper alignment, stability and mechanical strength of the insulator assembly.
- Leakage path – the leakage path provides extra surface distance and improved pollution performance. This is by creating a longer electrical path along the insulator’s outer surface.
- Grading rings – grading rings work in areas with high voltage post insulators to help distribute the electrical field. This helps reduce the risk of electrical stress concentrations and corona discharge.
Features of a post insulator
The insulators have several features that contribute to the reliability in transmission lines. Together they help to ensure the safe, efficient and effective transmission of electricity in different networks. The following are the common features of the post insulator.
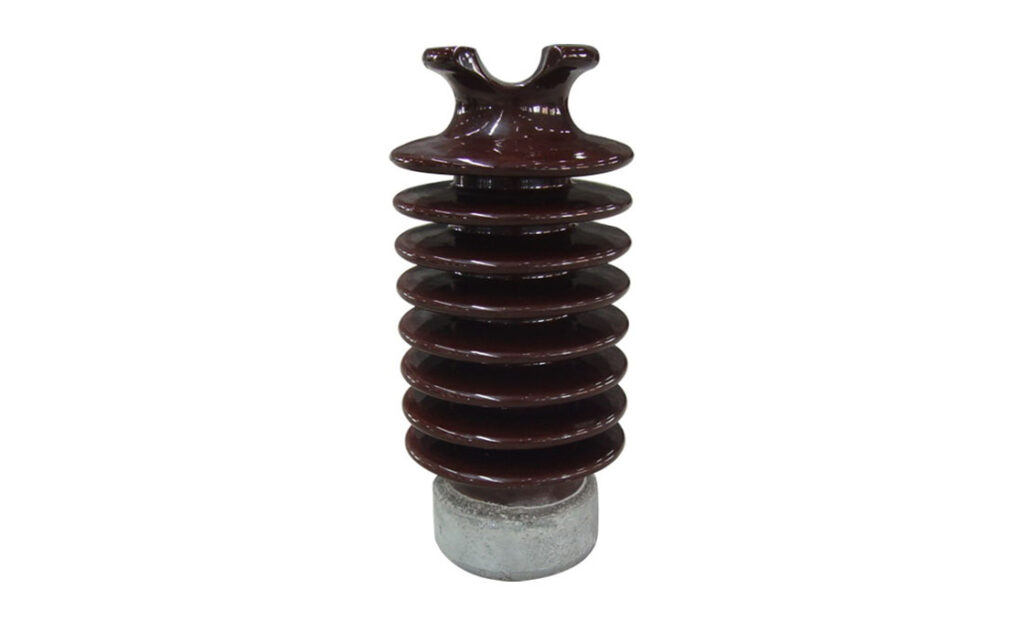

- Compatibility – the insulators have designs to support structures and conductors used in transmission systems.
- High dielectric strength – they have high dielectric strength which allows them to withstand high voltage levels.
- Electrical insulation – the insulators provide insulation between the conductors and support structures. This helps to prevent current leakage and ensures the safe electricity transmission.
- Mechanical strength – the insulators are able to withstand mechanical stresses. This is to ensure structural integrity and reliability.
- Corona control – post insulators have proper design and materials that help to control corona discharge. This helps to reduce power losses, audible noise and damage to insulator surfaces.
- Lightweight – lightweight post insulators reduce the load on supporting structures and simplifies installation.
- Ease of installation – the insulators have metal end fittings for easy mounting onto support structures.
- Weather resistance – they are from materials that are resistant to environmental factors. These include moisture, UV radiation, pollution and temperature fluctuations. This helps to ensure long-term reliability under various conditions.
Types of post insulators
There are two main types of post insulators used on the overhead transmission lines. selection of the insulators depends on the material they are from. They include porcelain, glass or polymer. The two main types of the post insulators are line and station post insulators. Other types vary depending on the designs. The following are the common types of the post insulator.

- Line post insulators – the insulators work in overhead lines to support the conductors. They also provide insulation between the conductors and supporting structures. They install in a series of insulators with each insulator providing voltage rating.
- Station post insulators – these are post insulators used in substations to support and insulate busbars. They are not as long as line post insulators but has wider diameter to hold higher currents. They consist of a solid insulating core made of porcelain or composite. They also absorb and distribute the mechanical forces along the length of the insulator.
- Tie-top line posts – these are insulators used for lower voltage applications up to 68kV. They connect and secure to the conductors using a top tie.
- Vertical clamp top-tie line posts – these insulators have a stud base and a clamp top. They mount on the top of the pole for support and insulation.
- Horizontal clamp top line posts – this is a vertical clamp top line post that inserts on the side of a utility pole. They may also have a clamp top and a gain base installed on the side of the pole.
- Brace post insulators – this is a combination of a suspension insulator and a horizontal line post. It has designs to provide support and insulation in specific configurations.
Functions and uses of a post insulator
Post insulators have several functions in electrical transmission and distribution systems. They help to ensure the safe, reliable and efficient transmission of electricity. It is important to understand these functions before selection. This helps to ensure your application meets all the necessary requirements. The following are the common functions of the post insulator.
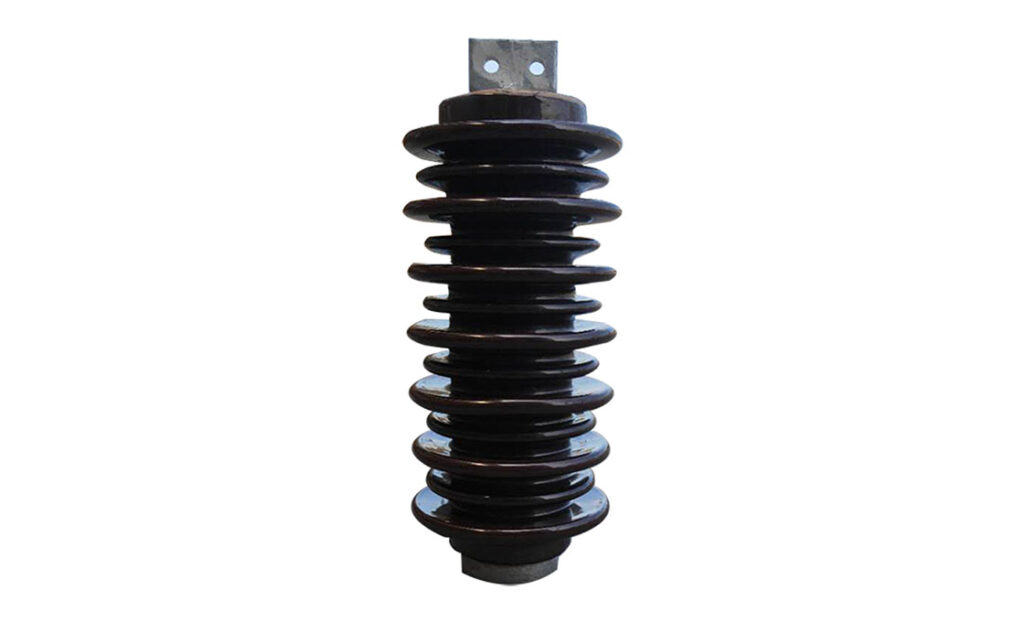

- Electrical insulation – this is the main function of the post insulator. Insulation helps to prevent current leakage and ensures the electricity transmits without loss.
- Creepage distance enhancement – they have sheds that increase the creepage distance along the surface. This helps to prevent flashovers caused from pollution, contamination and moisture.
- Weather protection – insulators are from materials that are resistant to environmental factors. This enables them to ensure long-term performance and reliability of the insulator.
- Durability – post insulators have designs to withstand the rigors of outdoor exposure and electrical operation. This is because they have high mechanical strength, thermal stability and resistance to physical damage.
- Mechanical support – the insulators support the weight of the conductors and provide mechanical stability. They also have designs to withstand the mechanical stresses from wind and ice.
- Corona control – post insulators have designs to reduce corona discharge which can lead to power loss and damage. The insulators help to maintain the integrity of the transmission system.
- Ease of installation – post insulators have metal end fittings that allow easy mounting onto the support structures and connection to conductors.
- Versatility – the insulators are available in various types and designs to suit different voltage ratings, environmental conditions and mechanical requirements.
Materials used in the construction of post insulators
Post insulators are from various durable materials that offer several advantages. This includes mechanical strength, electrical properties and resistance to environmental factors. The selection of insulator material depends on factors such as voltage ratings, mechanical needs and costs. Additionally, it is advisable to seek professional help whenever in doubt. The following are the common materials used in the construction of post insulators.
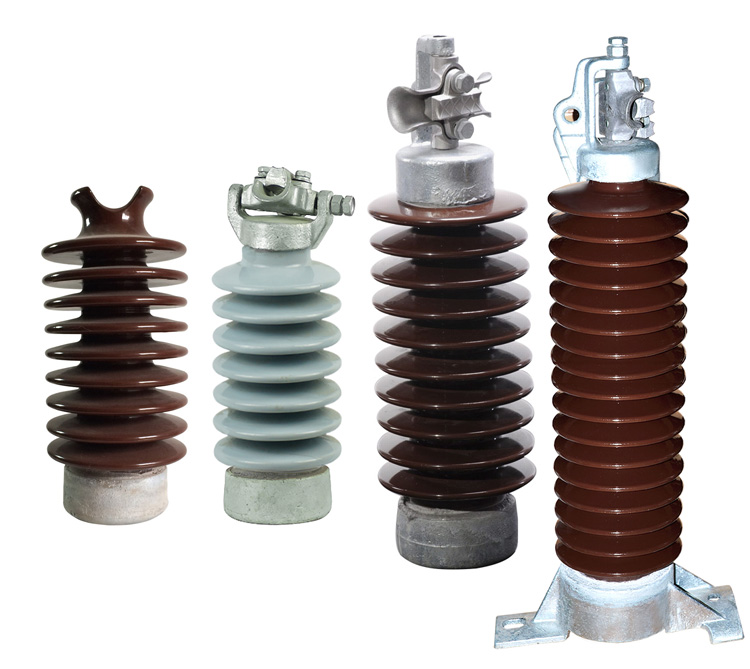

- Porcelain – this is the most used material in the manufacture of post insulators. Porcelain offers mechanical strength, high dielectric strength and resistance to moisture. Porcelain post insulators work in medium to high voltage applications.
- Glass – glass insulators provide electrical and mechanical properties and are lighter in weight. They have a smoother surface to enhance self-cleaning properties. Glass post insulators work in high voltage transmission lines.
- Composite materials – these include materials such as silicone rubber or epoxy resin reinforced with fiberglass. Composite insulators are light weight, resistant to damage and better pollution performance. They work in medium to high voltage applications.
- Ceramics – this includes advanced materials such as alumina or silicon nitride. They offer mechanical strength, thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion. Ceramic insulators find use in high voltage and high temperature applications.
- Hybrid materials – these include materials such as porcelain or glass with polymer coatings. They help to ensure specific properties such as mechanical strength, weather resistance and pollution performance.
Frequently asked questions
A post insulator is a component used to provide electrical insulation between conductors and support structures. Its main purpose is to prevent current leakage and ensure safe transmission of electricity.
Post insulators are from materials such as porcelain, glass, polymer, ceramics and hybrid materials.
Post insulators prevent flashovers by increasing the creepage distance along their surface. This reduces the risk of flashovers caused by pollution, contamination or moisture.
