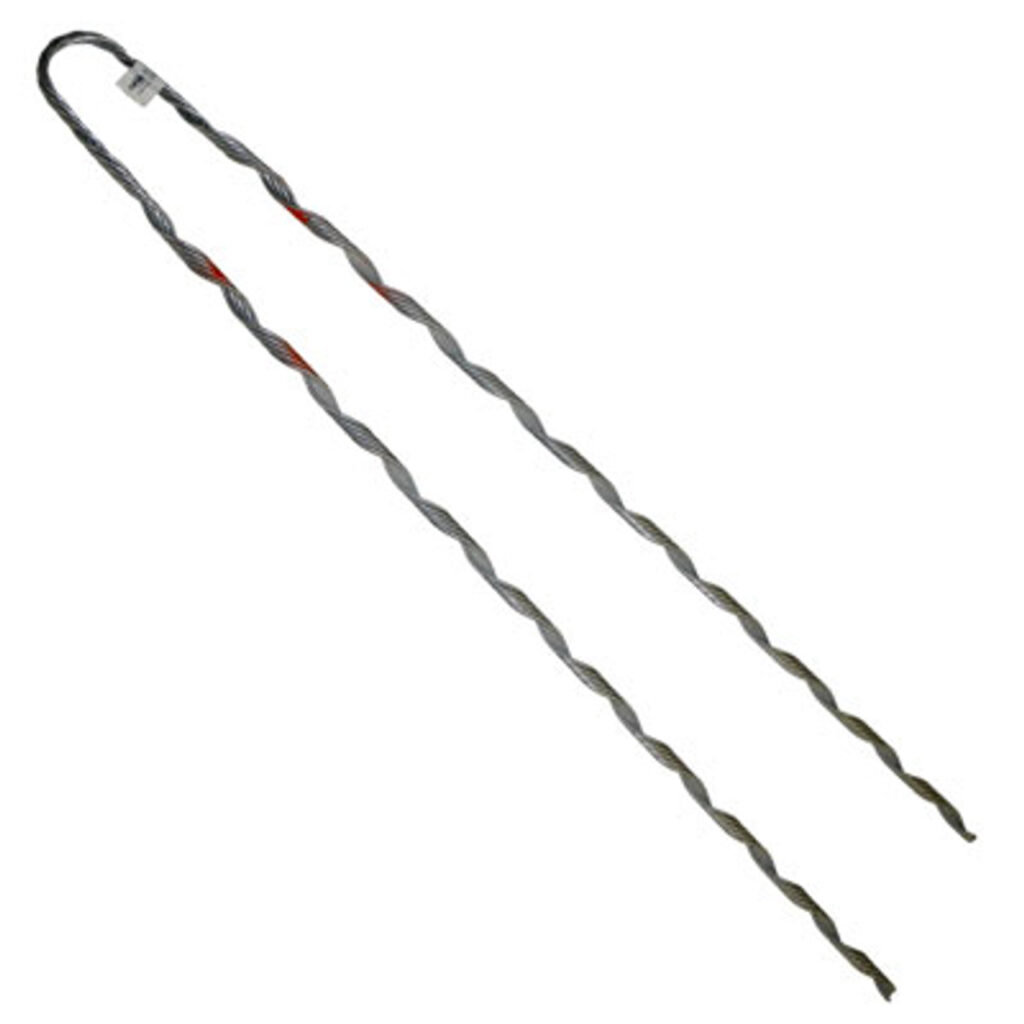

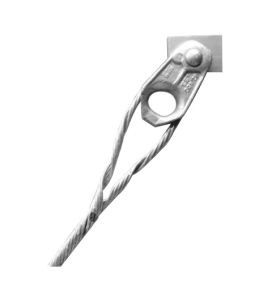
A big grip dead end is a type of formed wire used in cable installation and management. This is in telecommunications, transmission lines and electrical industries. It is also known as a suspension grip or as grip. A big grip dead end consists of a metal sleeve of grip applied to the end of a cable. It has grooves of teeth that grip the cable when it inserts. Big grip dead ends work in applications that need suspension of anchoring. They provide reliable and durable means to terminate cables to prevent accidents. Big grip dead ends also help manage the tension by gripping the conductor and distributing the forces. Big grip dead ends for transmission lines are from materials that withstand mechanical stresses. They are from materials such as high-strength steel, aluminum, galvanized steel or composite materials.
Components of a big grip dead end
Big grip dead ends have components designed to anchor and terminate the end of a conductor. The grips work with several elements to ensure the safety and reliability of the application. The following are the common components found in a big grip dead end.

- Grips – these are the main components responsible for gripping the conductor in place. They consist of serrated jaws or clamps made of high strength materials such as steel. Its design helps prevent slippage or detachment of the conductor.
- Preformed rods – preformed rods are from high strength materials like aluminum steel. They provide structural support to the grip. This helps maintain the desired shape and alignment of the dead-end assembly.
- Dead end sleeves – these are protective sleeves made of insulating materials. These materials include rubber or composite polymers. They cover and insulate the gripping area where the conductor is in contact with the grip.
- Thimble – these are protective metal fittings placed inside the grip to protect the conductor from abrasion or damage. It provides a smooth surface for the conductor to rest against during installation and tensioning.
- Socket or eye – this is the part that attaches to the support structure. It has a loop which a fastening mechanism inserts through to secure the dead end.
- Structural components – these include bolts, nuts, washers and other fastening hardware. They secure the components together and provide structural integrity.
- Anchoring hardware – extra anchoring hardware helps to secure the dead-end assembly to the supporting structure.
- Protective coatings – most of the components have coatings to enhance their resistance to corrosion and abrasion.
Features of the big grip dead end
The grip dead ends have various features that help ensure reliable and secure termination of conductors. Their design contribute to the reliability and efficiency of the transmission infrastructure. This is to ensure the safe and uninterrupted delivery of electrical power. The following are big grip dead end features.
- Material – the big grip is from high strength materials such as aluminum or steel. These materials ensure durability and resistance to environmental factors. They help ensure they can support and secure the conductors under heavy loads.
- Gripping mechanism – this is including the serrated or grooved surfaces that secure the grip to the conductor. It ensures a tight and reliable hold to prevent slippage or detachment. This is especially in harsh weather conditions.
- Corrosion resistance – they also have coatings with corrosion resistant materials. This is to protect them from the effects of environmental exposure.
- Versatility – the dead ends are versatile to suit various applications and environmental conditions.
- Resistance to environmental factors – they have designs to resist environmental factors. This is including UV radiation, extreme temperatures and other conditions.
- Tension support – the dead end contributes to the tension support of guy wires. It also helps to maintain the proper tension levels required for the stability of the transmission system.
- Ease of installation – the big grip dead ends have straightforward assembly and attachment to the support structure. This helps streamline the installation process and reduces labor costs
- Design – they have various designs to accommodate a range of guy wire sizes to provide flexibility in their application.
- Strength and load capacity – their designs allow them to withstand high tension and loads associated with transmission towers. They are also built to withstand the rigors of outdoor use and exposure to various factors. This is including UV radiation, temperature fluctuations and mechanical wear.
Why use big grip dead ends?
Using big grip dead ends provides safety, reliability and compliance with standards. This helps to ensure the functioning of the transmission line infrastructure and delivery of electricity. The following are the benefits of using big grip dead ends.
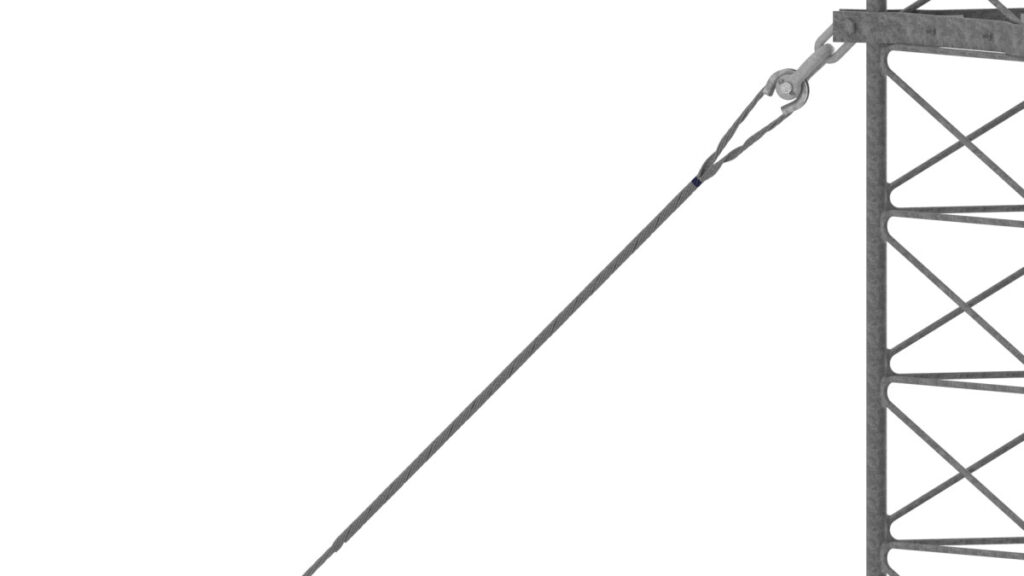

- Safety – big grip dead ends anchor conductors to the support structures. This is to prevent conductor sag, swing or looseness.
- Prevention of damage – proper installation of the big grip dead ends distributes the mechanical stresses along the length of the conductor. This helps reduce the risk of damage or fatigue failure and maintenance needs.
- Environmental impact mitigation – big grip dead ends play a role in reducing the environmental impact of transmission lines. They help prevent the risk of conductor damage or failure. Reduced maintenance and repair activities contribute to lower resource consumption.
- Damage prevention – proper installation helps distribute mechanical stresses along the length of the conductor. This reduces wear and tear on the conductor and promote a longer service life.
- Construction and maintenance efficiency – using big grip dead ends streamline the installation and maintenance of the lines. the components have designs promoting easy assembly and attachment to support structures.
Accessories used with big grip dead ends
Big grip dead ends work with a variety of accessories to enhance their functionality, improve installation efficiency and ensure longevity. Additionally, it is advisable to consult with professionals for guidance on the best accessories to use. The following are the common big grip dead end accessories.
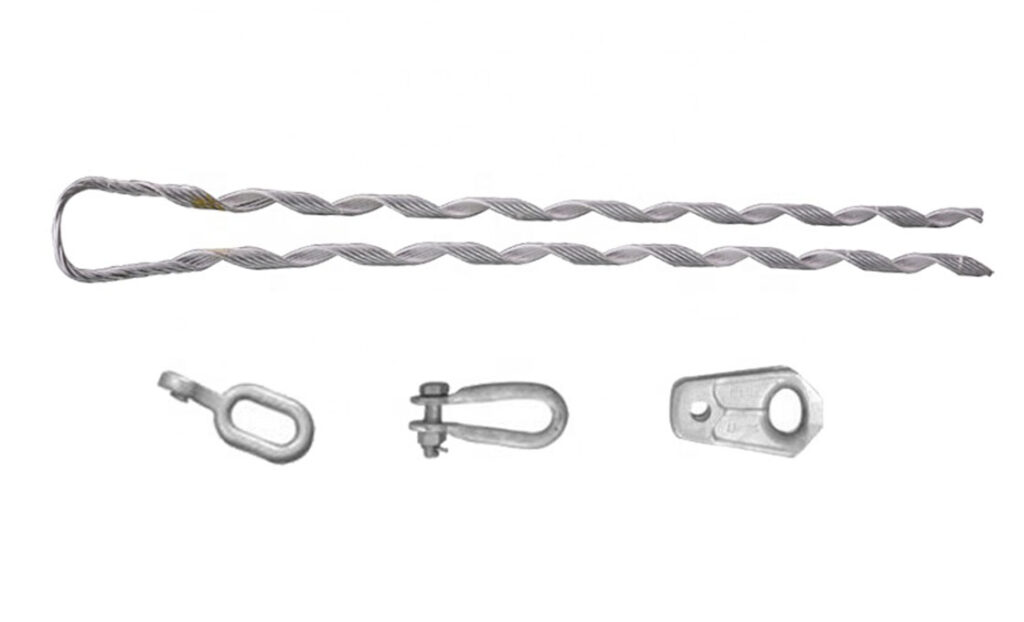

- Armor rods – these help to protect the conductor where it enters the grip assembly of the big grip dead end. They are from galvanized steel or aluminum and help distribute the mechanical stresses along the conductor. This helps to reduce the risk of damage or wear at the termination point.
- Dead end insulators – these help to prevent electrical current from flowing through the support structure to the ground. They provide insulation between the conductor and the support structure. This is to ensure safe and reliable operation.
- Guy wire clamps – guy wires help provide extra support and stability to the transmission towers. Guy wire clamps help to attach the guy wires to the structure to ensure proper tension and alignment.
- Tensioning tools – these help during the installation and tensioning of the conductor within the grip assembly. The tools help to ensure proper tensioning of the conductor and help achieve the desired performance.
- Anchor rods – these rods are from high-strength steel and install deep into the ground or embedded in concrete foundation. They help to provide stability and resistance to lateral and vertical forces.
- Corrosion protection products – these include coatings, tapes and sealants. They protect the components from corrosion and environmental degradation.
- Suspension clamps – these clamps help support the weight of the conductor between the transmission towers. They attach to the conductor and provide a secure attachment point to the support structure. This helps to maintain the desired tension and alignment of the transmission line.
Various types of grip dead ends
There are various types of big grip dead ends designed to meet specific application requirements. They each offer unique features and advantages for different overhead transmission line applications. Also, it is advisable to consider conductor size and type, installation needs and tension forces when selecting the dead ends. The following are the common big grip dead end types.

- Swage dead end – these use mechanical swaging techniques to create a permanent connection between the grip and conductor. Swaging involves compressing the metal around the conductor creating a secure and low resistance joint.
- Bolted dead end – this type uses bolts and nuts to secure the grip to the conductor. This dead end offers a strong reliable connection and is commonly used for medium to high voltage transmission lines.
- Armor rod dead end – armor rod dead ends incorporate extra components known as armor rods. They provide extra protection and support. This reduces the risk of abrasion and damage
- Compression dead end – compression dead ends use compression fittings to secure the grip onto the conductor. They have designs that create a tight and durable connection without the need for bolts or other tools.
- Hydraulic dead end – these use hydraulic pressing methods to achieve a reliable and robust connection. They work in high tension application and handle significant loads.
Frequently asked questions
A big grip dead end is a hardware component used to anchor and terminate the end of a conductor. Its purpose is to ensure the reliable and safe operation of the transmission line. This is by gripping the conductor and providing a stable attachment point to the structure.
Performance characteristics include strength and load capacity, secure gripping, corrosion resistance and durability.
