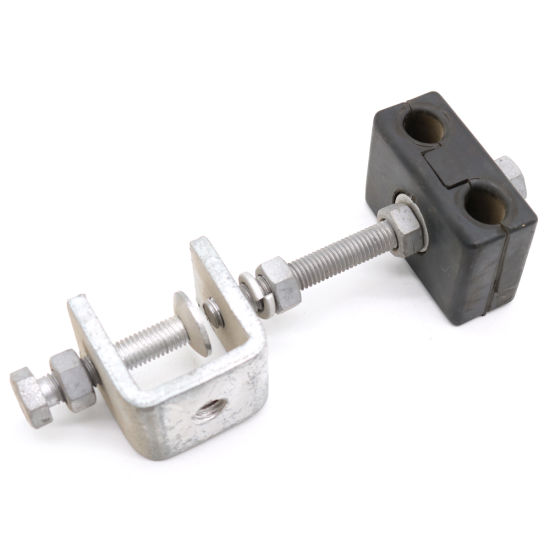

A downlead clamp is a hardware used to secure and guide fiber optic cables as they transition from the transmission line. It is also known as a downlead cushion, cable clamp or wire clamps. Downlead clamps provide support and protection for the fiber optic cables. It prevents excessive movement, vibration and abrasion that could damage the delicate fibers. The clamps ensure proper cable routing and alignment on the transmission lines. This helps reduce stress on the cable and maintain signal quality. Common types include bolted downlead clamps, suspension downlead clamps and compression downlead clamps. The choice of the clamp depends on factors like cable type and diameter, location and environmental conditions. Downlead clamp may work in various of our applications in the electrical industry. This is including telecommunication lines, power lines, construction and renewable energy projects.
Materials used in the manufacture of downlead clamp
Downlead clamps have specific designs to withstand environmental conditions and provide reliable support for cables. There are various materials used in the manufacture of downlead clamps. The selected materials also depend on factors like application, environment and specific requirements. Additionally, it is advisable to consult with industry experts on guidance on the best material for your application. The following are the common materials for downlead clamps.

- Galvanized steel – this material provides strength, durability and resistance to corrosion. The process of galvanization includes coating the steel with a layer of zinc to protect it from rust and corrosion. This makes it suitable for outdoor applications and harsh environmental conditions.
- Aluminum – this is light weight and provides good corrosion resistance. This makes it suitable for outdoor applications.
- Composite materials – this includes materials like fiberglass-reinforced plastics. They offer strength, durability and corrosion resistance. They are common for clamps used for fiber optic cables.
- Stainless steel – this material provides excellent strength and durability. It works in applications such as marine or coastal environments. It is mainly found in clamps like U-shaped clamps, wrap-around clamps and tower clamps.
- Copper – this is an excellent conductor of electricity and it works in applications where conductivity is necessary. Copper clamps may feature coatings to improve its resistance to environmental factors.
Properties of the downlead clamp
Downlead clamps have various properties that contribute to the provision of support and security to cables. The properties vary depending on factors like material used, design specifications and intended application. The properties help to ensure long-term reliability and safety. The following are the common properties of available downlead clamps in the market.
- Weather resistance – downlead clamps should be capable of withstanding various weather conditions. This is including rain, snow, wind and extreme temperatures. This is without compromising their functionality and structural integrity.
- Durability – the clamps should be durable and resistant to corrosion, rust and degradation over time. This helps to maintain their functionality even in various exposures.
- Corrosion resistance – materials such as galvanized steel, stainless steel and aluminum protect the clamp from rust and corrosion. This is because they install in environments with temperature fluctuations, moisture, UV radiation and mechanical wear.
- Strength – the clamps should have strength to support the weight of the cables or wires. This ensures the cables remain in place without sagging or slipping.
- Electrical insulation – downlead clamps have electrical insulation to prevent contact between conductive materials. They also help reduce the risk of electrical hazards or short circuits.
- Installation ease – they should have features that offer easy installation and compatibility with different cable sizes and types.
Testing and certifications for downlead clamps
This practice helps ensure the essential electrical components meet industry standards for safety, performance and quality. The available testing depends on the region and intended application for the clamp. The tests provide certifications from recognized regulatory bodies or standards organizations. Having the certifications for the downlead clamps contributes to the quality and performance of electrical installations. Also, it is advisable to consult with industry professionals for the recommended certifications. The following are the various testing and certifications for downlead clamps.

- Material testing – these tests assess the properties of the materials used in their construction. They include tensile strength, corrosion resistance and durability. This ensures the materials meet the specified standards for performance and reliability.
- Mechanical testing – this assesses the structural integrity and mechanical properties of downlead clamps. This is including their ability to withstand mechanical stress, load capacities and resistance to deformation.
- Electrical testing – some of the clamps need electrical testing to verify their electrical insulation properties. They also ensure they provide adequate protection against electrical hazards.
- Environmental testing – these tests check the performance of downlead clamps under different environmental conditions. This including temperature extremes, moisture, UV exposure and chemical exposure.
- Manufacturer’s testing and quality control – most manufacturers conduct internal testing and quality control measures. This is to ensure the downlead clamps meet their specified requirements.
- Certifications – the clamps may need to get certifications from recognized standards organizations. This is to show compliance with industry standards and regulations. Some certifications for the clamps include UL certifications, CE certification and IEC certifications.
Cons of the materials used for downlead clamps
As mentioned earlier, choosing the right material for downlead clamps depends on various factors. These include application requirements, environmental conditions, budget constraints and desired properties. Additionally, it is crucial to consult with qualified professionals for guidance on the best materials for your application needs. The following are the common pros and cons of materials used for downlead clamps.

- Galvanized steel – this material can be heavier compared to other materials. This may affect installation and handling. It may also corrode over time in harsh environments.
- Stainless steel – this material is more expensive compared to other materials. They may also show magnetic properties which could be a consideration in some applications.
- Aluminum – this is not as strong as steel and may limit its use in heavy-duty applications. It is more expensive than galvanized steel and they can experience galvanic corrosion.
- Plastic – these materials are resistant to corrosion and rust, easy to handle and provide electrical insulation. However, they may not have same level of strength as metal clamps and may degrade at high temperatures.
Technical specifications for downlead clamps
The technical specifications for downlead clamps vary depending on various factors. These include specific application, industry standards and manufacturer’s design. Consult with manufacturers documentation for specific details of a particular downlead clamp. additionally, ensure adherence to relevant industry standards and regulations. This is to ensure the safety, and performance of downlead clamps in electrical installations. The following are the factors that influence the technical specifications for downlead clamps.
- Size and capacity – this includes the dimensions of the clamp such as length, width and diameter. It also includes the capacity to accommodate the cables or wires of specific sizes and types.
- Corrosion resistance – this includes specifications related to the clamp’s resistance to corrosion, rust and environmental factors. This is including exposure to moisture, chemicals or UV radiation.
- Electrical properties – this includes specifications related to electrical insulation, conductivity and compatibility.
- Material – this includes the wide range of materials used for the manufacture of the clamps. This is including galvanized steel, stainless steel and aluminum.
- Load rating – this is the greatest load the downlead clamp can support without failure. This is in pounds or kilograms.
- Temperature range – this is the range of temperatures within the clamp can operate without degradation.
- Installation requirements – this includes the installation method, specific hardware or tools and guidelines for proper placement.
- Environmental considerations – these are specifications related to the clamp’s performance under environmental conditions. This includes resistance to UV exposure, moisture ingress and extreme weather conditions.
- Manufacturer information – some manufacturers offer technical specifications for the downlead clamps. Some information includes name, model, batch code or part number.
Technical specifications
| Code | Cable Diameter (mm) | Weight(KG) | Material |
| JYTC-05-B | 9.0-13.3 | 0.8 | Rubber, Galvanized steel |
| JYTC-07-B | 13.4-17.7 | 0.8 | Rubber, Galvanized steel |
| JYTC-10-B | 17.8-19.7 | 0.8 | Rubber, galvanized steel |
Frequently asked questions
Downlead clamps work in electrical installations to secure and support cables or wires. This is to ensure they remain in place and prevent sag or slip under various environmental conditions.
Common materials for downlead clamps include galvanized steel, stainless steel, aluminum and plastic. Each material offers different properties such as strength, corrosion resistance and weight.
The size of the downlead clamp depends on factors such as the diameter and type of cable to secure. Select the clamp that accommodates the size of the cable and meets the load requirements of the applications.
