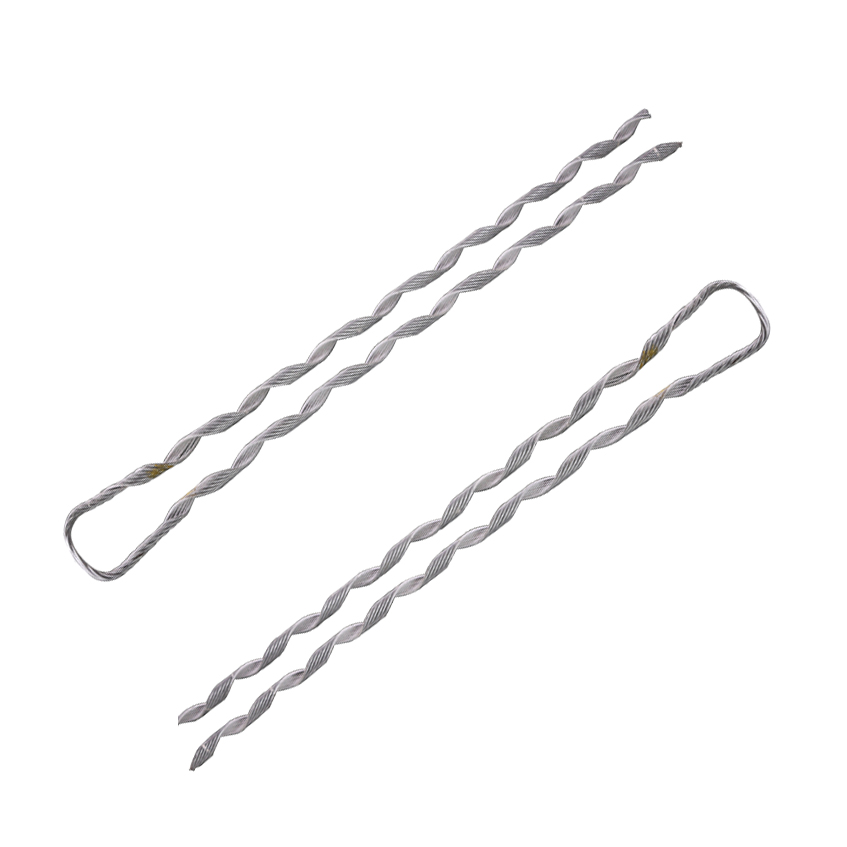

A distribution grip dead end is a component used for securing and supporting conductors at the endpoints. It refers to the installation of a grip mechanism at the endpoint of a conductor cable. It helps to secure the conductor cable to the support structure. This ensures the conductor remains in place even under high tension. The dead ends contribute to the safe and reliable operation of the transmission line. Its function is to grip the conductor, reduce stress concentrations and improve reliability. It features serrated jaws or clamps that grip the conductor. Distribution grip dead ends are from high-strength materials. These include steel, aluminum or composite materials and consists of jaws. These materials have designs to withstand the mechanical forces and environmental conditions.
Properties of the distribution grip dead end
The properties of the dead end grip help to ensure its effectiveness and durability. These properties aid in supporting and terminating conductor cables in overhead transmission lines. This helps to ensure the reliability and safety of the electrical distribution system. The following are the common properties of the distribution grip dead end.

- Material composition – distribution grip dead ends are from high-strength materials. The materials should have mechanical properties. This is including high tensile strength, durability and resistance to corrosion.
- Load rating – dead end grips have ratings for specific load capacities to ensure they withstand mechanical forces. The load rating should be enough to support the weight of the conductor.
- Insulation properties – distribution grip dead ends need insulation properties to prevent electrical arcing. Insulating materials provide electrical insulation and ensures safe operation.
- Installation features – the grip dead end should have designs for easy installation. These include ergonomic handles, quick-release mechanisms and compatibility with standard tools. They help to ensure proper installation and tensioning of the grip dead end.
- Grip design – the grip design holds onto the conductor cable without causing damage. It includes features such as serrated jaws, specialized grooves or gripping inserts. These help to enhance the grip strength and reduce slippage.
- Environmental resistance – the dead end grips should be resistant to environmental factors. The dead ends may feature protective coatings or finishes to enhance corrosion resistance.
- Compatibility –the dead ends should be compatible with the size and type of conductor used. It should be able to accommodate the diameter and configuration of the conductor without damage.
Selection of distribution grip dead end
Proper selection of the distribution grip dead end requires careful consideration. Consider these factors aid to ensure compatibility, reliability and effectiveness. These considerations help to meet the specific requirements of your application. Additionally, it is advisable to seek professional help when selecting the dead ends. The following are the factors to consider when selecting the dead ends.

- Cost effectiveness – assess the cost-effectiveness of the grip dead end. Consider factors like initial purchase cost, long-term durability and maintenance requirements.
- Installation ease – check the ease of installation and maintenance requirements of the grip dead end. The dead end should have features such as ergonomic handles, quick-release mechanism and clear installation instructions.
- Compatibility – the grip dead end should be compatible with the system design and integration requirements. Ensure the grip is compatible with the size, type and configuration of the conductor cable.
- Material quality – select a dead end made from high -quality materials. Ensure the materials provides mechanical strength, corrosion resistance and durability.
- Supplier reputation – choose grip dead ends from reputable manufacturers. They should follow relevant industry standards and regulations.
- Load rating – determine the greatest load capacity required for the distribution grip dead end based on the tension forces. The dead end grip should have a load rating that exceeds the anticipated loads to ensure safety and reliability.
- Application requirements – determine the specific requirements of the application. Consider factors like voltage level, mechanical stresses and the weight of the conductor.
- Conductor type and size – consider the type of conductor you will be working with. This may include bare conductors, insulated cable or guy wire. Ensure the grip dead end is compatible with the conductor’s diameter, configuration and construction.
Installation practices for grip dead ends
The installation process for distribution grip dead ends involves several steps. Following the steps helps to ensure a safe and effective installation of distribution grip dead ends. Also, it is important to follow manufacturers guidelines and specifications for dead ends. The following is a basic installation guide for distribution grip dead ends.
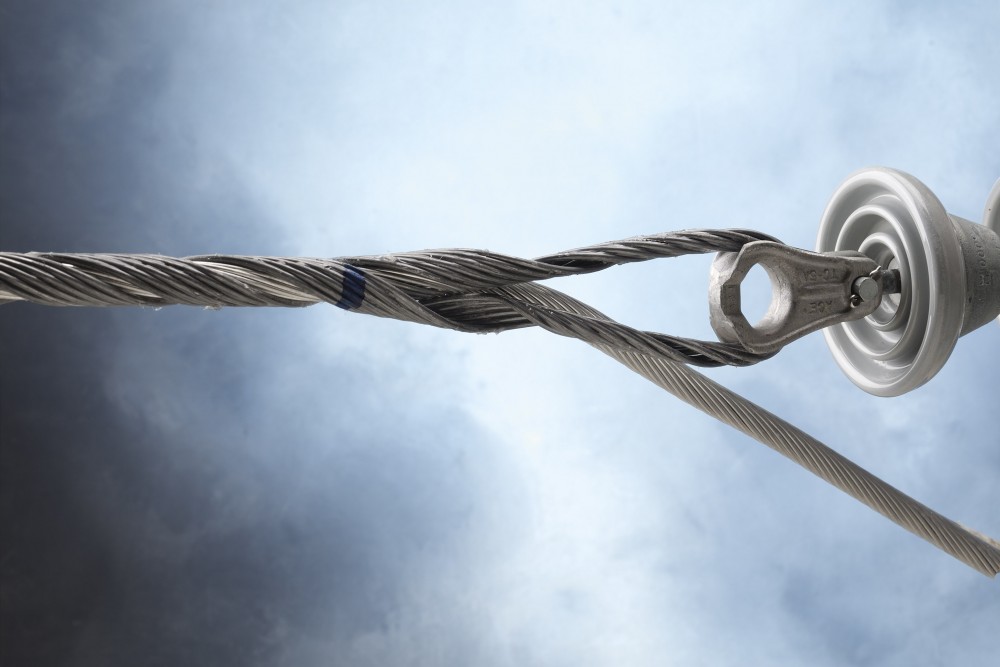

- Preparation – gather all the necessary tools required for the installation. This is including distribution grip dead end, wire grips, fasteners, wrenches and safety equipment.
- De-energization – work with power utility to schedule planned outage. This helps to ensure safety of the installation and personnel.
- Dead end positioning – determine the correct location for installing the distribution grip dead end. Ensure it positions securely and aligned with the conductors.
- Secure the conductor – use wire grips to secure the conductor in place. This requires precise positioning for proper engagement.
- Dead end attachment – securely attach the distribution grip dead end to the conductor. This may involve use of nuts, bolts and other hardware provided.
- Tightening – tighten the grip dead end to the conductor to prevent any movement using suitable wrenches.
- Alignment – verify that the distribution grip dead end aligns with the conductor. This also helps to ensure their effectiveness.
- Inspection – conduct visual inspections of the installed distribution grip dead end. Check for any signs of damage, defects or irregularities.
- Testing – conduct any necessary testing to ensure the distribution grip dead end functions as expected.
- Documentation – keep detailed records of the installation including the date, location, type of dead end installed and any testing performed.
Maintaining distribution grip dead ends
Maintenance for distribution grip dead ends helps to ensure their continued effectiveness and reliability in supporting cables. Implementing these practices helps to ensure the continued performance and reliability of the dead ends. This is important as it contributes to the safety and efficiency of the electrical distribution systems. Additionally, it is important to conduct professional maintenance and inspection of the distribution grip dead ends. The following are the basic maintenance processes for the dead end grips.

- Establish a regular inspection schedule based on the manufacturer’s recommendations and environmental conditions.
- Check the structural integrity of the dead end and look for signs of deformation, bending or other issues compromising strength.
- Verify the distribution grip dead end remains properly aligned with the conductor which can lead to stress.
- Assess the electrical integrity of the dead ends on live lines and ensure there are no signs of arcing.
- Consider the specific environmental conditions in the installation area. Assess the impact on the distribution grip dead end.
- Inspect distribution grip dead ends for visual signs of wear, damage or corrosion and missing components.
- Clean the dead ends to remove any debris, dust or contaminants to prevent corrosion and ensure proper functioning.
- Apply corrosion resistant coatings to protect the dead end from corrosion in areas with harsh environmental conditions.
- Inspect the distribution grip dead ends for any signs of wear or damage. replace the damaged armor rods to maintain the dead ends performance.
- Maintain detailed records of inspections and maintenance activities. This is including dates, observations and any maintenance actions taken.
Testing distribution grip dead ends
Distribution grip dead ends undergo several tests to ensure their functionality, reliability and compliance with standards. The tests also help the dead ends to contribute to the efficiency of the electrical distribution system. the following are the common tests for distribution grip dead ends.
- Visual inspection – conduct a visual inspection to check for any visible signs of damage, wear or deformation. Check for cracks, corrosion, loose or missing hardware and other causes that may affect the grip’s performance.
- Tension testing – use a tensioning device to measure the tension applied to the conductor cable. Apply tension while tracking the force exerted on the cable to ensure it fall within the specified range.
- Functionality testing – test the functionality of the grip dead end by simulating installation and tensioning procedures.
- Load testing – perform load testing to check the grip dead end’s ability to withstand the greatest load it may encounter. Monitor for any signs of deformation, slippage or failure of the grip dead end under load.
- Material analysis – perform material analysis to check the composition and mechanical properties of the materials used.
- Corrosion resistance testing – conductor corrosion resistance testing to evaluate the grip dead end’s ability to withstand exposure to various factors.
Frequently asked questions
A distribution grip dead end is a device used to anchor and support conductor cables at their endpoints. It consists of a gripping mechanism that holds onto the cable and attaches to a support structure. It prevents the cable from sagging or becoming loose.
The main properties include material composition, grip design, load rating, environmental resistance and insulation properties.
Dead end grips undergo tests such as tension testing, load testing, corrosion resistance and functionality testing.
