
A distribution grip dead end is a component found in both electrical distribution and transmission networks. Distribution grip dead ends provide a secure connection point for conductors. They also aid to withstand weather conditions like wind and ice loading. They contribute to the structural integrity and reliability of the overhead wire system. Dead end grips are also useful for terminating the ends of overhead cables. This serves to maintain tension in the line and supports the weight of the conductors. Distribution grip dead ends are also used to terminate the ends of high-voltage transmission wires. They have designs to endure high levels of strain and mechanical stress. Common varieties include bolted, compressed, preformed, and guy grip dead ends.
Parts that comprise the distribution grip dead end
The components of distribution grip dead ends differ according on their design and manufacturer. The components work together to create a safe and stable attachment point. High-quality components contribute to the integrity and performance of the distribution line. The distribution grip dead ends consist of the following components.
- Body – the primary body consists of a robust frame or housing that holds the grasping mechanism. Also, it provides structural support for the conductor’s attachment.
- Gripping mechanisms – this is a component that holds the conductor in place. To avoid slippage, the mechanisms contain serrated jaws, wedges, and other characteristics.
- Attachment hardware – dead-end grips need hardware to attach to the support structure. This helps to secure the dead end to a utility pole or transmission tower. These include bolts, nuts, washers, clamps, and straps.
- Insulating material – grip dead ends may have insulating material for electrical isolation. This insulation prevents electrical arcing and assures the safety of the line.
- Corrosion protection – the dead-end grips may be corrosion resistant. These contribute to increased durability and longevity. This protects the dead end from external elements like moisture and salt.
- Tension adjustment mechanism – distribution grip dead ends include a tension change mechanism. This enables for finer control of the tension applied to the conductor.
- Labeling and markings – dead end grips may have labels and markings with information. This includes manufacturer’s specifications, part numbers, and installation directions.
Materials used in the building of distribution grip dead ends.
Distribution grip dead ends are from materials that are strong, durable, and suitable. A variety of factors influence material selection. These include application requirements, environmental factors, and financial considerations. The following materials are commonly used in the manufacture of distribution grip dead ends.

- Steel – this is the most used material for distribution grip dead ends. This relates to its superior strength and durability. Steel dead ends aim to withstand mechanical strains and loads. It may also have coatings or galvanized to increase corrosion resistance.
- Aluminum – aluminum dead end grips are lightweight but durable. They also provide good corrosion resistance with the help of protective coatings.
- Stainless steel – this has exceptional corrosion resistance, particularly in severe or corrosive conditions.
- Bronze – this is a copper alloy that has strong corrosion resistance and mechanical qualities. It may also work for its aesthetic value and resilience to wear and tear.
- Composite materials – some dead ends may contain composite materials due to their lightweight and corrosion-resistant qualities.
- Insulating materials – this is including plastics or rubber. They cut electrical conductivity between the conductor and the support structure.
Accessories for distribution grip dead ends.
There are various accessories and fittings that are compatible with distribution grip dead ends. This attempts to simplify installation, improve performance, and ensure safety. Also, choose the appropriate accessories based on the application’s requirements. The following are common attachments for distribution grip dead ends.
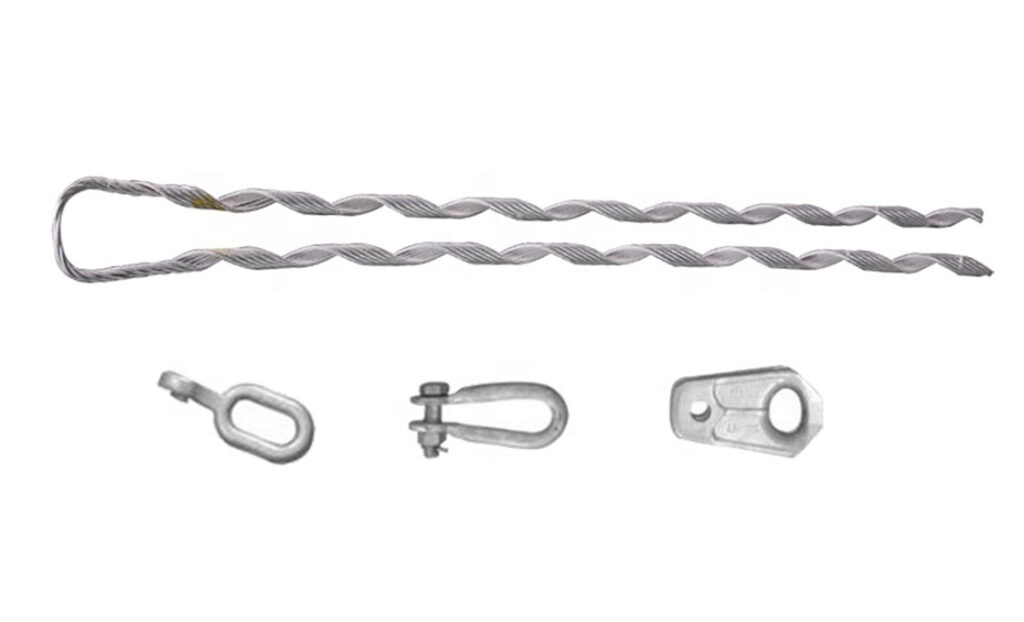

- Grips – these are the primary components of the dead end, serving to hold the conductors in place. They come in a variety of configurations, including helical grooves, serrated jaws, or clamps.
- Preformed rods – these are metallic rods or strands that serve to strengthen the grip. They add strength and stability to the grip dead end assembly.
- Installation tools – these include wrenches, sockets, torque wrenches, and tensioning tools. These contribute to the appropriate installation and tightening of bolts, nuts, and other fasteners.
- Thimbles – these are metal sleeves or loops that fit into the grip dead end assembly. It creates a smooth surface for the conductor to go through. This protects the grip from making direct contact with the conductor and causing damage.
- Suspension insulators – these work with dead end grips in suspension distribution lines. They provide both electrical isolation and mechanical support.
- Connecting links – these are the components that attach the grip dead end assembly to the supporting structure. They are from robust, corrosion-resistant materials such as steel.
- Anti-theft devices – they are devices fitted on the distribution grip dead end to prevent theft and vandalism. These devices contribute to the integrity of the distribution line and prevent unwanted access to electrical infrastructure.
- Cotter pins – these are small metal fasteners used to attach and lock components of the grip dead end assembly together. They keep the grips, prepared rods, and armor rods from becoming loose.
Distribution grip dead ends for ADSS/OPGW cables.
Distribution grip dead ends function in ADSS and OPGW cables to terminate them in electrical distribution systems. ADSS and OPGW cables work in telecommunications, data transmission, and electrical distribution networks. Additionally, these dead ends contribute to the safe and reliable operation of telecommunications and data transmission networks. The following describes the use of distribution grip dead ends in ADSS and OPGW cables.
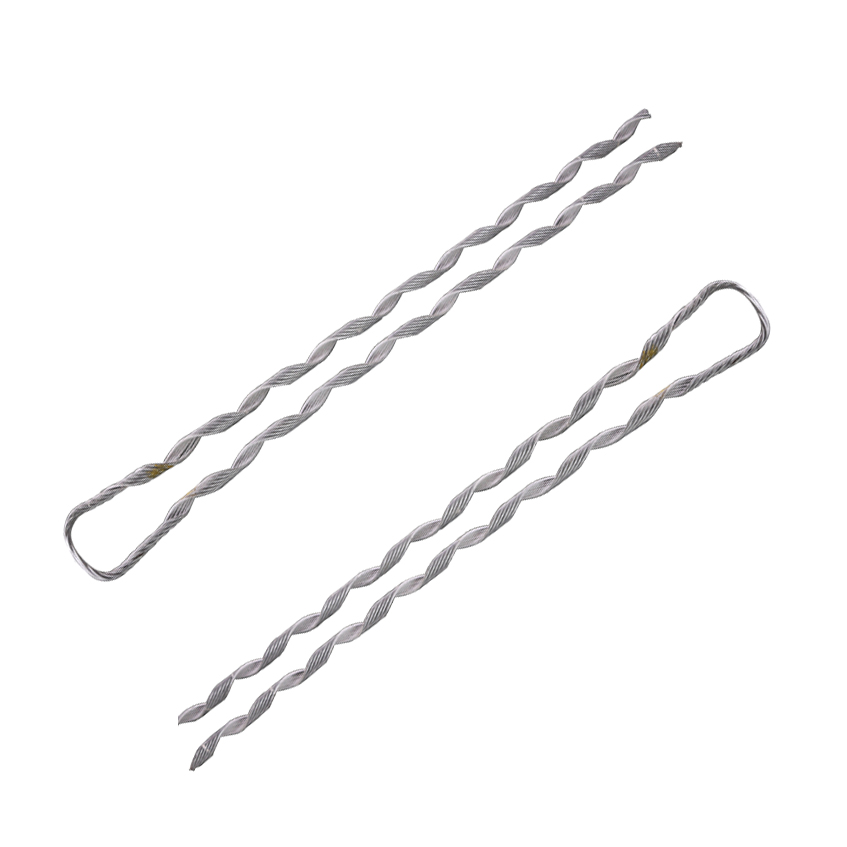

ADSS distribution grip dead ends
ADSS cables have designs to be self-supporting. Distribution grip dead ends for ADSS cables aim to meet the special construction and installation requirements. The dead ends contain a grasping device that holds the ADSS cable. It clamps the cable without injuring the optical fibers. Distribution grip dead ends may include elements like as insulating materials to promote electrical separation.
OPGW distribution grip dead ends
OPGE cables support both electrical grounding and optical fiber connection. The dead ends for OPGW cables can accommodate both electrical and optical functions. They also contain a gripping device to secure the OPGW cable. It accomplishes this while preserving electrical continuity. Distribution grip dead ends for OPGW may include corrosion-resistant materials to protect against environmental influences.
Factors that influence material choices for dead end grips.
There are various elements that determine the materials used for distribution grip dead ends. The proper material selection helps to ensure that they meet performance and durability. Consider these factors when selecting materials to meet the application’s specific requirements. Additionally, when in question about the optimal material selection, it is advisable to seek professional help. The following are some common factors that influence material selection for dead ends.

- Mechanical strength – the material should be strong enough to bear tension and stresses. Consider the conductor’s weight, wind and ice loads, and tension fluctuations.
- Electrical conductivity – the materials used for dead ends must not interfere with electrical conductivity. Use materials like aluminum alloys to cut resistance in the distribution line.
- Temperature stability – distribution grip dead ends must withstand temperatures ranging from freezing cold to high heat. The material chosen should keep its mechanical qualities and performance.
- Cost considerations – high-performance materials with exceptional properties are more expensive. Manufacturers must combine performance requirements with financial constraints to provide cost-effective solutions.
- Corrosion resistance – distribution grip dead ends may face exposure to moisture, salt, UV radiation and other elements. Materials like stainless steel, aluminum alloys or coated steel ensure longevity and reliability.
- Weight – the weight of the dead ends can impact installation procedures and load on the support structure. Lightweight materials help to reduce the weight of the dead ends without sacrificing strength.
- Fatigue resistance – dead end grips face cyclic loading due to wind, conductor movement and other factors. Materials with good fatigue resistance properties withstand these cycles.
- Regulatory compliance – the dead ends must follow relevant industry standards and regulations. They should comply to standards such as IEC, NESC and ISO standards.
Frequently asked questions
A distribution grip dead end is a component used to terminate the ends of conductors and attach them to the support structures. It serves to provide a secure attachment point for the conductor, support its weight and manage tension.
Dead ends for ADSS and OPGW cables have designs to provide secure termination and support while maintaining structural integrity and optical performance.
Materials used for distribution grip dead end include steel, aluminum alloy, stainless steel and composite materials. These materials offer mechanical strength, corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity.
Common accessories include installation tools, guy wire grips, suspension insulators, protective coatings, spacer dampers and anti-theft devices.
