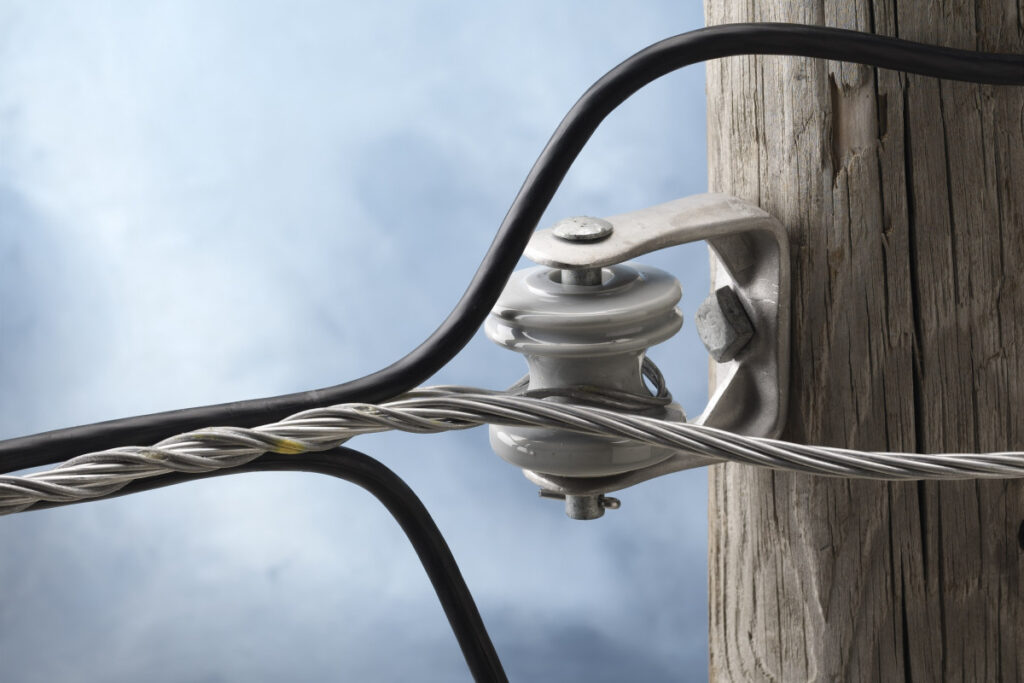

A service grip dead end is a crucial component used in the installation and maintenance of overhead transmission lines. It helps in securing conductors wires that carry electrical current and other cables at endpoints. A service grip dead end anchors and terminates conductors on poles, towers or other structures. It has designs to hold the conductor in place to prevent it from slipping or loosening over time. It consists of a loop end, materials, helical structure and materials for durability. Using service grip dead end ensures security, reliability and easy installation. Service grip dead ends are from materials like steel, aluminum or composite materials. These materials provide durability and resilience. They find use in applications such as overhead transmission lines, utility poles and telecommunications.
Key features of a service grip dead end
A service grip dead end has features to ensure the reliability and safety of electrical distribution systems. Its design, material composition and ease of installation contribute to its effectiveness. The following are the key features of the service grip dead end.
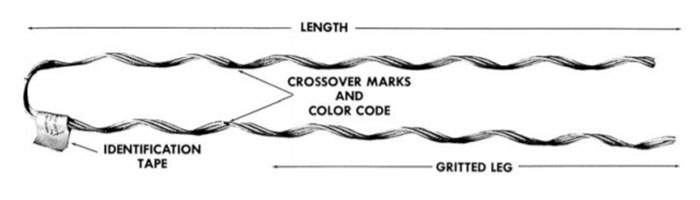
- Preformed helical structure – the dead end consists of a set of helical-wound preformed wires. The helical design also ensures the pressure distributes along the conductor.
- Material compatibility – the grip is from materials that are compatible with the conductor. This helps to prevent galvanic corrosion. Common materials include aluminum, galvanized steel or aluminum-clad steel.
- High tensile strength – the dead ends have designs to handle high tensile loads. They help to ensure the conductors remain anchored. They also provide the necessary mechanical stability to maintain the integrity of the line.
- Ease of installation – the preformed nature of the grip allows for easy and quick installation. This is without the need for special tools or advanced skillset. This features reduces installation time and labor costs.
- Flexibility and adaptability – service grip dead ends are suitable for various conductor types. This versatility makes them applicable across different transmission line configurations.
- Reliable performance – the preformed design ensures a consistent and reliable grip on the conductor. The materials and design ensures performance reliability under a wide range of weather conditions.
- Electrical conductivity – the grip dead ends have designs to provide good electrical conductivity. This ensures a reliable electrical path for grounding purposes to reduce electrical arcing.
- Minimal maintenance – the dead ends need minimal maintenance after installation. This is due to their strong construction which ensures long-term durability and stability.
- Safety features – the purpose of the dead ends is to terminate the conductor. The reliable anchoring by the grip helps prevent accidents related to failing conductors.
Functions of using a service grip dead end
Service grip dead ends have designs to perform several functions in overhead transmission lines. Their main role is to anchor and terminate electrical conductors. They also ensure the stability and reliability of power systems. Additionally, they help to ensure the transmission lines can deliver reliable power under a wide range of conditions. The following are the functions of using a service grip dead end.

- Secure termination of conductors – grip dead ends provide a secure termination point for conductors. This prevents the conductors from moving or slipping out of place. This is to maintain the integrity of the electrical networks.
- Tension management – they aid in managing and maintaining the proper tension of the conductors. The grip ensures the tension distributes along the conductor to reduce stress concentrations.
- Load bearing – the dead ends have designs to support the mechanical loads exerted by the conductors. This is including the weight of the conductors and extra loads from wind and thermal expansion.
- Vibration dampening – the helical design of the service grip dead ends aid in dampening vibrations. This reduces wear and tear on the conductors to prevent damage overtime.
- Enhanced electrical safety – the grip dead ends prevent accidental disconnections that could lead to power outages. A secure grip reduces the risk of electrical arcing at termination points.
- Line integrity maintenance – service grip dead ends ensure the continuity and integrity of the transmission line. This is by providing stable termination points for uninterrupted power supply.
- Ease of installation and maintenance – the design of the service grip dead ends allows for quick and easy installation. They also need minimal maintenance which lowers the maintenance costs and efforts.
- Cost efficiency – the ease of installation and minimal maintenance needs contribute to cost savings.
Common types of service grip dead ends
Service grip dead ends come in various types and designs to suit specific application needs and conductor types. These types help to ensure the stability and reliability of the electrical infrastructure. Some of these types offer ease of installation and high strength permanent terminations. Additionally, the choice of grip depends on factors such as conductor type, load requirements and environmental conditions. The following are the common types of service grip dead ends used in overhead transmission lines.

- Preformed dead end grips – these consist of helical-preformed wires that wrap around the conductor. They have designs to handle high mechanical loads and provide a strong grip on the conductor. Preformed dead end grips are suitable for terminating overhead conductors.
- Automatic dead end grips – these use a self-activating clamping mechanism that grips the conductor. They also contain spring-loaded jaws or wedges that grip the conductor. They work in medium and high voltage transmission lines that need quick installation.
- Compression dead end grips – these grips use a sleeve compressed around the conductor using hydraulic tools. This provides a permanent, high strength termination for the conductor.
- Wedge dead end grips – these use a wedge driven into a housing to grip the conductor. It also has designs to handle high tension loads and provide a secure termination.
- Bolt-type dead end clamps – these uses bolts and clamps to secure the conductor to provide a mechanical hold. They are suitable for terminating both overhead and underground cables.
- Guy dead end grips – these have designs to terminate guy wires used for supporting structures like poles. They are suitable for telecommunications and utility structures to secure guy wires.
Applications areas of the grip dead ends
Service grip dead ends are components used in various applications within the electrical transmission and distribution industry. They also work in areas that need reliable mechanical and electrical connections. They are versatile and reliable which makes them indispensable in ensuring stability. Additionally, it is important to understand their functions in various applications before selection. The following are the common application areas of service grip dead ends.
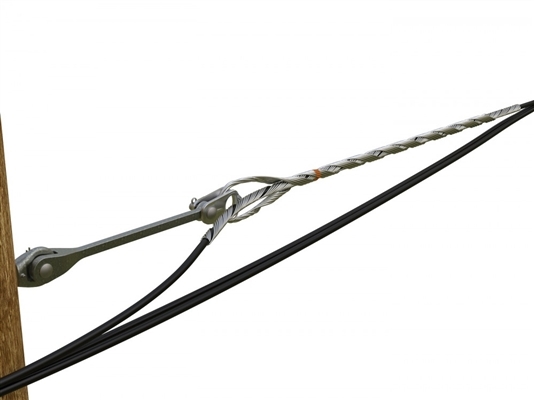

- Overhead transmission lines – dead ends work in high-voltage and medium voltage transmission lines. They also provide a secure connection that ensures the stability and reliability of the transmission system. They help in conductor termination, tension management and line tensioning.
- Distribution lines – service grip dead ends anchor conductors at various points along the distribution line. This includes at end poles and at points where the direction of the line changes. They work in pole termination, service drops and line changes.
- Telecommunications – the grip dead ends help to secure and end cables for telephone lines, internet cables and other lines. They ensure stable connections to reduce the risk of service interruptions.
- Railway electrification – the dead ends work in electrification systems where they anchor and end overhead contact wires. They also help to end and tension contact wires that supply power to electric trains.
- Guy wire applications – the dead ends help to secure and end guy wires that provide structural support to poles, or towers.
- Renewable energy installations – service grip dead ends help to secure and end cables that send power from generation sites to the grid.
- Utility poles and structures – the dead end grips serve in securing and terminating cables and wires on utility poles. They are also versatile and allows for quick and reliable termination of cables.
Challenges and issues facing use of service grip dead ends
There are several challenges and issues related to using service grip dead ends. These can affect the reliability, safety and efficiency of the transmission lines. The following are the challenges related to using service grip dead ends.
- Installation challenges – incorrect wrapping during installation can lead to ineffective gripping and potential conductor slippage.
- Material compatibility – using incompatible materials for the dead end and conductor can lead to galvanic corrosion.
- Environmental and weather impacts – the service grip dead ends may face ice loading and temperature fluctuations. This can lead to excessive tension and cause conductor slippage.
- Electrical issues – this may include electrical arcing and grounding problems. They can lead to damage of the conductors and compromise their safety.
- Cost considerations – high quality dead ends can lead to the increase of the initial cost of transmission line construction.
Frequently asked questions
Service grip dead ends help to anchor conductors, manage tension, support mechanical loads and dampen vibrations.
High quality service grip dead ends provide reliable, secure and long lasting connections to reduce the risk of failure.
Common challenges include incorrect installation, need for specialized tools and the need for skilled labor.
