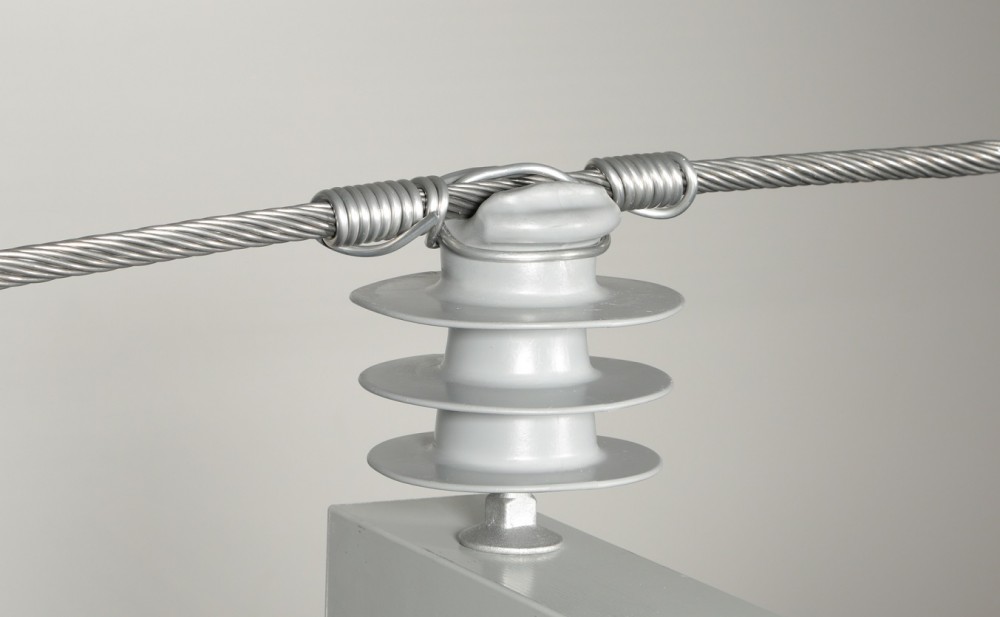

A line guard is a component used to protect and maintain the integrity of the conductors. A line guard protects the lines from lightning strikes. It shields the conductors from mechanical damage caused by external factors like wind or galloping. It also helps to reduce aeolian vibration and other dynamic movements. This can lead to fatigue and failure of the conductor. Line guards offer protection against environmental influences like salt, pollution and bird contact. By doing so, they prevent physical damage and reduces vibrations to extend the lifespan of the transmission lines. Use of line guards help to save costs in the long term by reducing the need for repairs and replacements. Line guards help to ensure the continuous and effective delivery of electricity on the transmission lines. Line guards are from materials like aluminium, copper, stainless steel, and composite materials.
Components of a line guard
The line guard has various components designed to provide protection and ensure the longevity of the conductors. They protect the conductors from mechanical stress, abrasion and other forms of damage. These components need regular inspections to ensure their continuous functionality. The following are the components of the line guard.
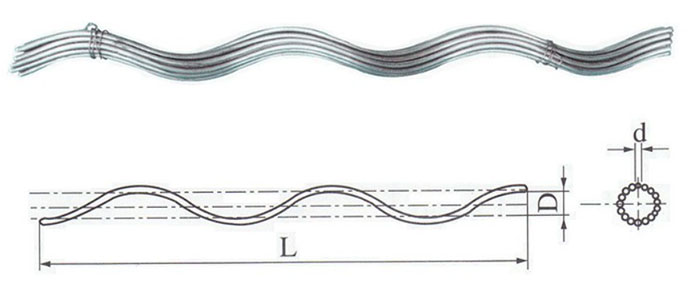
- Helical rods – this is the core component of the line guard which consists of many helical rods. They wrap around the conductor for protection. They are from materials such as aluminium, galvanized steel or stainless steel. Its design matches the diameter and shape of the conductor to ensure a comfortable fit for protection.
- Preformed end fittings – these fittings secure the ends of the helical rods to ensure they stay in place after installation. Its design grips the conductor without causing damage to help in distributing the stress along the length of the line guard. Its materials help to maintain consistency in mechanical and corrosion resistance.
- Spacer rods – these help to maintain a uniform distance between the helical rods and enhance the structural integrity of the guard. Their design helps to ensure the helical rod remains spaced around the conductor.
- Binding wires – these help to secure the helical rods to the conductor at specific points. This is to provide extra stability and ensure the line guard remains in place. They have designs to wound around the helical rods and conductor to keep the assembly stable.
- Protective coating – some of the guards may have an extra protective coating. This is to enhance resistance to environmental factors. Its design applies to the surface of the helical rods and fittings to provide an extra layer of protection.
Functions of the line guard on transmission lines
Line guards serve several functions in the protection and maintenance of transmission lines. They help to ensure the reliability, longevity and efficient operation of the infrastructure. They help to prevent conductor damage and prolong the lifespan of the infrastructure. These functions help the line guards to function to the reliability of the power transmission system. The following are the functions of the line guard.

- Mechanical protection – line guards protect the conductor from mechanical abrasion caused by environmental factors. They also prevent wear and tear at points where the conductor comes into contact with hardware.
- Vibration mitigation – line guards help to dampen aeolian vibrations. These include low-amplitude, high frequency oscillations from wind. Vibrations can lead to conductor fatigue and failure. They also reduce the impact of galloping from wind and ice loading.
- Stress distribution – line guards distribute mechanical stress over a larger are of the conductor. This reduces the risk of localized damage or failure. They also help prevent the conductor from breaking under stress.
- Environmental protection – line guards protect the conductor from corrosion caused by environmental factors. This is including moisture, salt and pollution. They also provide a barrier that can protect the conductor from damage by birds perching on lines.
- Electrical performance – the guards also protect the conductors from mechanical and environmental damage. They help to maintain the electrical integrity of the conductor to ensure efficient transmission of electricity. Line guards keep the conductors in good condition to reduce the electrical losses.
- Ease of inspection and maintenance – line guards serve as visible indicators of potential issues. This makes it easier for maintenance crews to identify and address problems before they lead to conductor failure. They also allow for easy installation and replacement to reduce downtime and labor costs.
Types of line guards
Line guards come in various types and designs to meet specific needs and applications. Each type of line guard serves to address different environmental conditions, mechanical stresses and conductor configurations. Also, it is advisable to choose the appropriate type of line guard based on environmental conditions. This helps to enhance the durability and reliability of their transmission infrastructure. Regular inspections and maintenance ensure the line guards continue to perform their protective functions. The following are the common types of line guards.
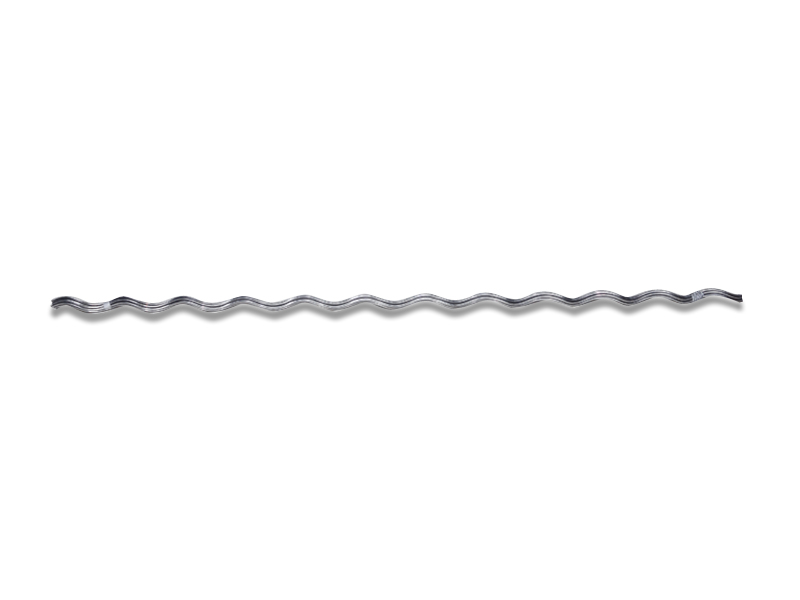

- Preformed line guards – these are helical-shaped rods that wraps around the conductor. They are from materials such as aluminium, galvanized steel or stainless steel. They have features to fit specific conductor sizes and are easy to install.
- Armor rods – the rods provide extra mechanical reinforcement in demanding applications. They are available in different lengths and diameters to match conductor specifications. They protect against wear and fatigue at crucial points on the conductor.
- Spiral vibration dampers – these consist of helically wound rods that act as dampers. They install at intervals along the conductor to dampen vibrations. They also work in areas with high wind activity to prevent conductor fatigue.
- Spacer rods – these rods install between conductors to maintain spacing and reduce mechanical stress. They help prevent conductors from clashing or getting too close.
- Thermal line guards – these have designs to protect conductors from thermal expansion and contraction. They provide protection against heat-induced sagging or damage. Thermal line guards find use in areas with high-temperatures.
- Insulated line guards – these incorporate insulating materials to prevent electrical faults. They also provide electrical insulation to prevent arcing and electrical discharge. They are effective in preventing bird contact and other wildlife-related issues.
Factors influencing the material selection of line guards.
Choosing the right material for the line guards involves balancing various factors. This is including environmental conditions, mechanical and electrical properties. It is also important to consider economic considerations, compatibility with conductors and specific application needs. Line guards are from materials such as steel, galvanized steel, aluminium and composite materials. Each of these materials offer different benefits and features. The following are the factors influencing material selection for line guards.

- Environmental conditions – materials for line guards must be resistant to corrosion especially in areas with salt air. Stainless steel and certain composites offer high corrosion resistance. The material should also be able to resist temperature variations and UV exposure.
- Mechanical properties – the material must have high tensile strength and durability to withstand mechanical stresses. It should also be flexible enough to wrap around conductors and resist fatigue.
- Electrical properties – the electrical conductivity of the material should not affect the performance of the transmission line. Materials with insulating properties prevent electrical faults and improve safety.
- Installation and maintenance – lightweight materials are easy to handle and help reduce labor costs and installation time. Select materials that need less maintenance and have longer service.
- Economic factors – consider the cost of the material selected. Stainless steel offers excellent durability and corrosion resistance but is more expensive. Also, consider the availability of the materials with shorter lead times.
- Compatibility with conductors – the thermal expansion properties of the line guard should be compatible with the conductor material. The selected material should prevent galvanic corrosion.
Challenges and issues of using line guards
There are several challenges that affect the use of line guards in overhead transmission lines. These challenges may affect their effectiveness and longevity. Also, it is advisable to address these challenges to enhance the effectiveness and reliability. The following are the challenges facing use of line guards.

- Integration with existing systems – ensure the line guards are compatible with existing transmission infrastructure.
- Performance limitations – line guards may not provide enough protection in extreme environmental conditions. They may need extra measures or enhanced designs to balance protection with minimal impact on conductor performance.
- Mechanical stress and damage – continuous exposure to dynamic mechanical stress can lead to material fatigue and failure.
- Material compatibility and durability – line guards should be from materials that resist corrosion, thermal expansion mismatch and environmental degradation.
- Installation challenges – installation of line guards needs precision to ensure proper fit and function. It is also important to use skilled personnel and specialized tools in some applications.
Frequently asked questions
A line guard is a protective component used to protect conductors from mechanical stress, abrasion and environmental factors. It helps to ensure the reliability and longevity of the transmission infrastructure.
Line guards serve several functions including mechanical protection, mitigation of vibrations, distribution of mechanical stress and protection against environmental factors.
Common types of line guards include preformed lien guards, armor rods, spiral vibration dampers and spacer rods.
