
A service grip dead end is a component that secures and terminates electrical conductors on cables. It ensures a safe and secure connection where the conductor terminates or changes direction. The dead end offers stability and stress in the lines. This ensures stability and tension in the lines. It also helps to avoid drooping and movement, which can lead to electrical problems. Service grip dead ends provide mechanical support, ensuring that the conductor remains in place under tension. Service grip dead ends have a helical form that wraps around the conductor, providing a solid grasp. They also use thimbles, eye nuts, and yokes to secure the grip to the support framework.
Performance features of a service grip dead end.
There are many methods for determining the performance characteristics of a service grip dead end. These qualities ensure the safe and effective functioning of overhead transmission lines. They also specify how the service grip dead end can fulfill its intended functions. The following are the primary performance features of a service grip dead end.

- Tensile strength – service grip dead ends have designs to handle high tensile loads to ensure they maintain the tension. The load capacity should match or exceed the expected tension in the cable.
- Durability and corrosion resistance – they are from high strength materials that offer resistance to wear and fatigue. The dead ends also come with protective coatings that are resistant to corrosion and help extend their lifespan.
- Grip efficiency – this ensures the service grip dead end maintains a firm hold on the cable without slipping. They also reduce the risk of localized stress points that could cause damage.
- Installation and maintenance ease – service grip dead ends do not need special tools for installation. This reduces installation time and labor costs for rapid deployment.
- Compatibility and versatility – dead end grips are available in different sizes and designs to match different cable types and diameters.
- Mechanical and electrical isolation – the grip provides mechanical stability without transmitting excessive forces to the cable. This also helps to protect the integrity of the cable’s core and prevent damage.
- Load retention and creep resistance – the dead ends have designs to prevent gradual slippage that could lead to loss of tension. High quality materials and designs ensure the grip does not deform.
- Vibration dampening – the service grip dead ends help to dampen vibrations caused by wind and other dynamic loads. This reduces the risk of fatigue and wear to enhance reliability.
Choosing the best service grip dead end
The proper selection of service grip dead ends guarantees that overhead transmission wires are stable and reliable. It requires careful consideration of cable specifications, environmental circumstances, and installation issues. Also, taking into account your application’s specific requirements helps to assure long-term durability and performance. The following are the considerations to consider when choosing service grip dead ends.
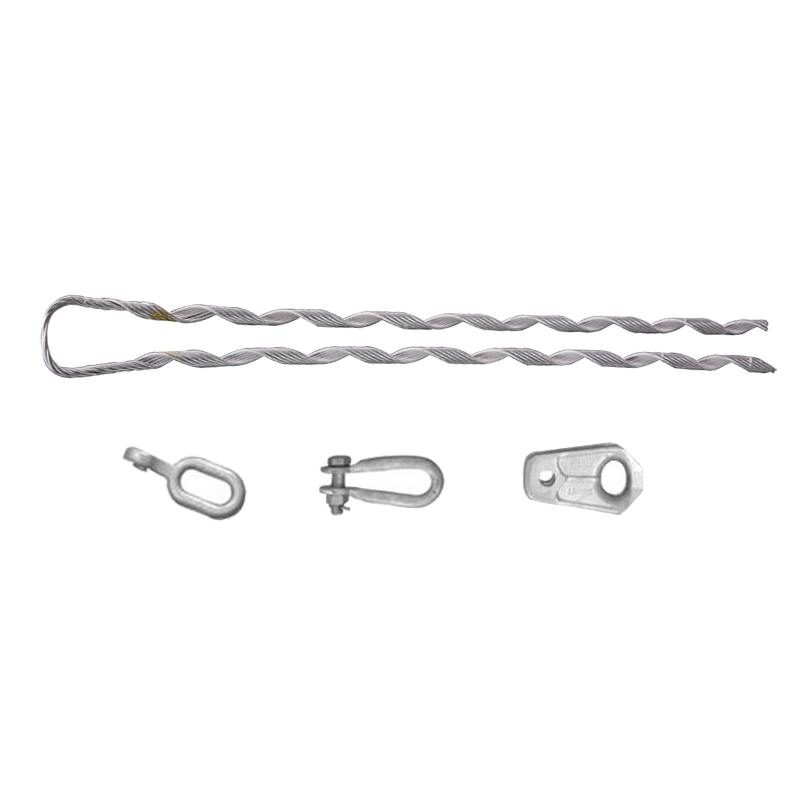

- Cable type and specifications – determine the cable type intended to work with the service grip. Measure the exact diameter of the cable to ensure the service grip dead end fits. Consider the material of the cables and its tensile strength.
- Environmental conditions – check the climatic conditions where the service grip dead end will install. Consider factors like wind speed, ice loading, temperature extremes and UV exposure. Select a service grip dead end with corrosion resistant materials.
- Mechanical requirements – calculate the greatest tensile load that the service grip dead end needs to support. Select a grip that can dampen vibrations for areas prone to high winds.
- Grip design – select the suitable grip design like preformed grips. They wrap around the cable t provide a secure and distributed grip. Check the dead end assemblies that include thimbles, clevises or eye nut for secure attachment to support structures.
- Load capacity and safety factors – ensure the service grip dead end can handle the greatest load with a suitable margin. Check that the grip meets relevant industry standards and safety regulations.
- Electrical requirements – ensure the service grip dead end provides enough electrical isolation. This is to prevent interference and maintain safety near power lines.
- Installation and maintenance factors – select a grip that is easy to install without the need for specialized tools. Choose a service grip dead end needs minimal maintenance.
Installation procedure for service grip dead ends.
Installing service grip dead ends is a critical step in assuring the secure termination of wires. Proper installation also helps to maintain the cable’s integrity, cut slippage, and assure long-term performance. Also, it is critical to adhere to the manufacturer’s installation requirements and recommendations. The following is a step-by-step installation guide for service grip dead ends.
- Work area preparation – ensure the work area is safe and clear of obstacles. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment including gloves, helmet, safety glasses and safety harness. Gather all the necessary tools and materials required for the installation.
- Cable preparation – inspect the cable for any damage, dirt, or debris. Use a measuring tape to verify the diameter of the cable. Trim the cable to the required length using cutting tools.
- Positioning and alignment of the service grip – position the service grip dead end at the cable’s end. The starting end of the grip should align with the mark on the cable. Check the pre-fit to ensure it fits and the cable is properly aligned with the grip’s end.
- Service grip installation – wrap the service grip dead end around the cable starting at the marked position. Make sure each wrap is snug and the grip applies without any gaps. Check that the grip attaches to the cable and there are no loose ends.
- Securing to the support structure – attach the necessary hardware to the grip’s looped end to connect to the support structure. Secure the grip and hardware to the support structure using a wrench to ensure all connections are secure.
- Inspection – conduct a thorough visual inspection of the installed service grip dead end. Verify that the cable is under suitable tension and no sag.
- Documentation – record the installation details including the type of service grip dead end used, cable specifications and other observations.
Maintenance and evaluation of dead ends.
Transmission systems’ long-term reliability and safety have the guarantee through regular maintenance and inspection. It also aids in detecting and addressing possible issues before they cause breakdowns. Additionally, professional maintenance is necessary to ensure sustained effectiveness. The following is a guide for maintaining and inspecting service grip dead ends.
Image
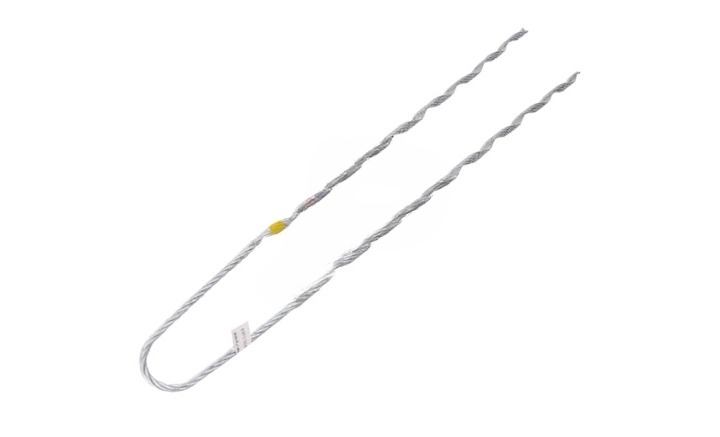

- Visual inspection – check the installation for slippage, corrosion, damage and cable condition.
- Mechanical inspection – verify that the cable is under appropriate tension and ensure the hardware is secure and not showing signs of wear.
- Environmental impact assessment – check the grip for signs of weathering or UV degradation. Check for any materials changes due to extreme temperatures.
- Electrical considerations – ensure the grip maintains proper electrical isolation and there is no sign of arcing. Verify the grounding and bonding are intact and functional.
- Cleaning and lubrication – clean any accumulated debris or dirt from the grip and cable. Apply lubricants to moving parts of the attachment hardware.
- Tightening – ensure all bolts and fasteners are tight to the manufacturers specifications. Adjust the cable tension to maintain proper alignment and load distribution.
- Corrosion protection – apply anti-corrosion coating to metal parts and replace any showing corrosion or wear.
- Replacement – replace damaged grips to ensure continued performance and safety. Upgrade any outdated hardware components.
Supplier info on the service grip dead ends.
Choosing the proper source for service grip dead ends is a critical decision that impacts reliability and performance. Careful study ensures that the provider meets all technical and operational requirements. The following criteria influence supplier selection for dead ends.
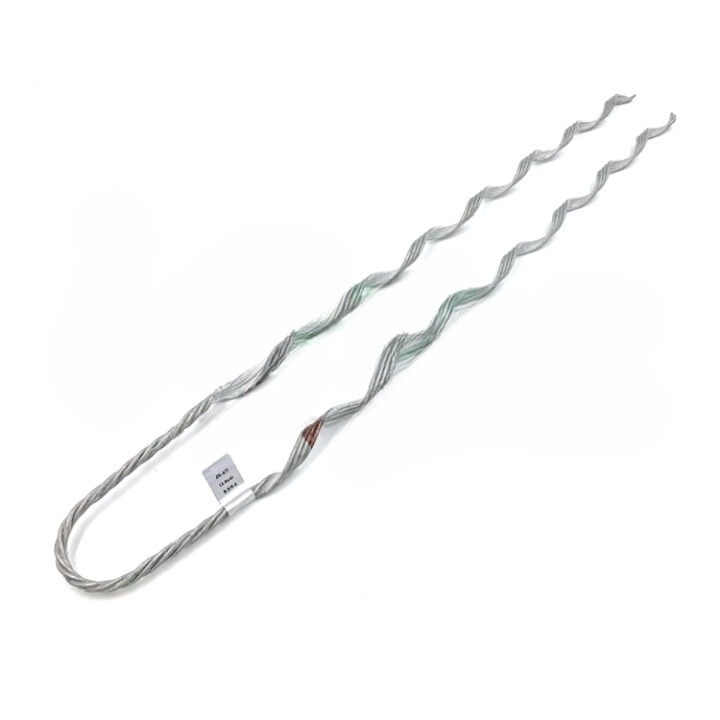

- Product quality and compliance – ensure the supplier uses high-quality materials that meet industry standards. Check if the supplier has a strong quality assurance process including testing for tensile strength and durability.
- Supplier reputation – research the supplier’s reputation in the industry and check for reviews, testimonials and case studies.
- Technical support – assess the supplier’s ability to provide technical support. This is including pre-sales consultations, installation support and ongoing maintenance advice.
- Product range and compatibility – the supplier should offer a wide range of service grip dead ends and more tailored options. The dead ends should be compatible with your existing systems and equipment.
- Lead times and availability – check the suppliers lead times for production and delivery. They should maintain enough inventory levels to meet your demands quickly.
Frequently asked questions
A service grip dead end works by wrapping around the cable in a spiral pattern, distributing the tensile load for a secure grip. It includes attachment hardware to connect to support structures and ensure the cable stays in place.
Suppliers with customization capabilities can provide grip tailored to your specific cable dimensions, environmental conditions and mechanical requirements.
