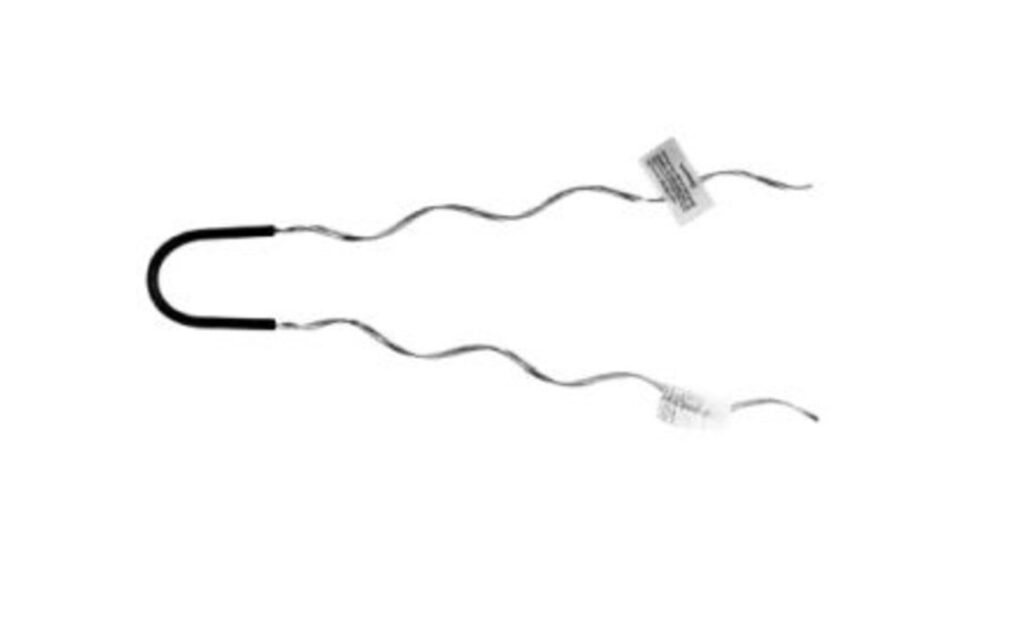
A slack span dead end serves to terminate primary, secondary or even neutral conductors. This helps to prevent the formation of a standing wave on the transmission line that could cause signal reflection. A slack span refers to a short length of conductor between two points where the tension is low. It provides easier access to the conductor for adjustment or repositioning. A slack span dead end facilitates easier connections, allows for flexibility in challenging terrains and reduces the mechanical load on support structures. It is from materials such as galvanized steel or aluminum which are resistant to aging and weather elements. Their designs are according to the ANSI standards or IEEE standards. Slack span dead ends work in the construction and maintenance of electrical transmission systems.
Features of the slack span dead end
A slack span dead end characterizes by several features that make it suitable for its role in terminating conductors. The features ensure stability, flexibility and safety of the transmission line. Understanding these features aids design, installation and maintenance of the electrical transmission lines. The following are the features of the slack span dead end.
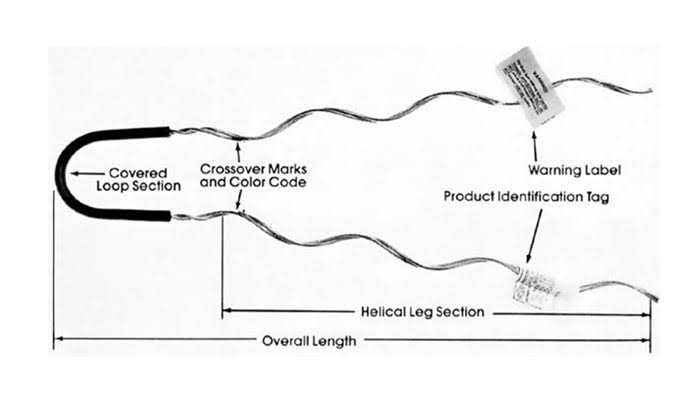
- Low tension on conductors – the slack span dead end should have minimal tension on the conductors. This is to reduce stress on the line and support structures. It also makes it easier to handle and less susceptible to mechanical damage.
- Increased sag – slack span dead ends have a higher degree of sag compared to regular spans. The increased sag allows for better accommodation of natural terrain variations.
- Short span length – the shorter span length reduces the tension and load on the conductor and support structures. This makes it easier to manage and adjust during installation and maintenance.
- Flexible conductor termination – the termination of the conductor at the slack span dead end is flexible for change. This aids in conductor alignment with substation equipment or other connections.
- Secure dead end clamps – dead end clamps attach to the conductor to ensure it is in place. This provides a reliable and strong anchor point to prevent the conductor from slipping.
- Insulators with high mechanical strength – the insulators used are able to handle electrical isolation and mechanical loads.
- Vibration damping – vibration dampers help to reduce oscillations caused by wind or other forces. This protects the conductor from fatigue and mechanical damage.
- Efficient grounding – a robust grounding system is in place to handle fault currents and prevent electrical hazards. Proper grounding ensures the safety of personnel and equipment to reduce the risk of damage.
Types of slack span dead end
There are different types of slack span dead ends used to meet different requirements related to termination. The selection depends on mechanical load, environmental conditions and specific applications. Each type of slack span ensures reliability and efficient termination of transmission line conductors. The following are the common types of slack span dead ends.

- Compression dead ends – these dead ends use a hydraulic or mechanical press to compress the conductor into a sleeve. It provides a secure and stable termination, can handle high mechanical loads and is resistant to loosening.
- Wedge dead ends – these use a wedge mechanism to grip the conductor to allow for easy installation and removal. It is suitable for medium to high-tension lines where quick installation is crucial.
- Bolted dead ends – these use bolts to secure the conductor in place where it clamps between two plates tightened with bolts. They commonly work in low to medium-tension applications.
- Automatic dead ends – these feature a helical structure that wraps around the conductor. The conductor terminates by inserting it into the preformed grips which tighten as tension increases.
- Suspension dead ends – these use insulators to suspend the conductor with the dead end components attached to the insulator string. It allows for flexibility in the line and reduces stress on the conductor.
- Vibration dampening dead ends – these dead ends incorporate vibration dampening elements. They protect the conductor from fatigue, extends lifespan and reduces maintenance costs related to vibration damage.
- Guyed dead ends – these use guy wires and anchors to provide extra stability to the structure supporting the dead end. They provide extra stability to the pole and reduces the load on the primary structure.
- Flexible dead ends – these dead ends allow for some degree of movement and flexibility at the termination point.
Application areas of span dead ends
Slack span dead ends provide flexibility, stability and reliability in various applications. Their applications range from managing difficult terrain to facilitating connections in urban and rural environments. Additionally, they work in challenging weather and environmental conditions. This is to ensure safe electricity transmission. The following are the application areas of slack span dead ends.
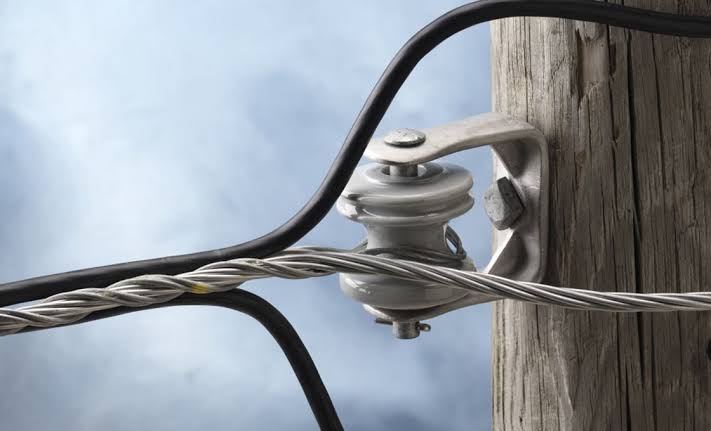

- Substation connections – slack span dead ends serve where transmission lines connect to substations. They provide a stable and adjustable connection point for the conductor. They also allow easier handling of the conductor for maintenance and adjustment.
- Difficult terrain and elevation changes – they help to accommodate differences in elevation. This is without imposing excessive tension on the conductors. They also reduce the risk of conductor breakage or excessive sag to ensure safe and stable transmission.
- Transition points between line sections – this is where the line transitions between different types of terrain. The dead ends help manage changes in mechanical loading and tension requirements. This helps to promote a smooth transition and reduces stress on the conductors.
- Line termination and dead end structures – slack span dead ends serve at the end of transmission lines. They help to anchor the conductor and manage the end-of-line mechanical forces.
- Junctions and taps – this is where lines branch off or where a tap changes from a main line. The dead ends accommodate branching without imposing excessive tension on the main line.
- Urban and industrial areas – slack span dead ends ease navigation around buildings and other obstacles. They avoid interference with existing infrastructure and eases integration with urban electrical networks.
- Agricultural and forested areas – slack span dead ends help manage the effects of natural growth and seasonal changes. The dead ends accommodate changes in the landscape without imposing high tension on conductors.
Supplier information for slack span dead ends
There are several suppliers for slack span dead ends in the market. The right supplier selection can impact the reliability, safety and cost effectiveness of your projects. There are various factors to consider when selecting the suppliers. TTF Power Systems provide a wide range of conductor hardware and formed wire for all your application requirements. Also, considering these factors helps to get high quality, durable and cost effective solutions for your projects. The following are the factors to consider when selecting slack span dead end suppliers.

- Quality and standard compliance – ensure the products follow the relevant industry standards. The materials used should be durable, high quality and suitable for specific environmental and mechanical conditions.
- Supplier reputation and experience – prefer suppliers with a proven track record and extensive experience in electrical transmission line components. Review customer’s feedback to gauge the supplier’s reliability, product quality and customer service.
- Product range and customization – the supplier should offer a wide range of slack span dead end products. This helps them to suit different specifications. Assess whether the supplier can customize products to meet specific needs.
- Technical support and service – ensure the supplier provides access to technical support. This helps with product selection and installation. They should also offer aftersales services for the products. This is including warranty coverage, maintenance support and availability of spare parts.
- Cost and value – compare prices among different suppliers to ensure competitive pricing without compromising on quality. Consider the cost including initial purchase price, installation, maintenance and lifespan of the product.
Challenges and issues facing the use of slack span dead ends
Slack span dead ends provide several benefits for flexibility and reduced tension. It yet presents other challenges and issues. These must be carefully managed to ensure the reliability and safety of overhead transmission system. Additionally, addressing these challenges involves a combination of careful design, regular maintenance and the use of high quality materials. The following are the challenges of using slack span dead ends.
- Mechanical stress and load management – slack spans have lower tension compared to regular spans. Insufficient management of mechanical stress can cause deformation or damage to poles.
- Environmental factors – slack spans are more susceptible to wind-induced vibrations and loadings. These can lead to oscillations and increased mechanical stress on conductors and supports. They may also accumulate more ice and snow due to their increased sag leading to higher mechanical loads.
- Installation and alignment challenges – ensuring precise alignment of slack spans can be challenging. The installation needs careful handling and specialized equipment to manage the reduced tension and increased sag.
- Maintenance and inspection – this may include accessibility issues, inspection complexities and higher maintenance costs.
Frequently asked questions
A slack span dead end is a type of conductor termination used to keep tension low, allow the conductor to have more sag and flexibility.
The components include conductor, dead end clamp, insulators, support structures and the anchoring system.
Features include low tension, increased sag, versatility, improved vibration damping and simplified maintenance.
