
A false dead end refers to a structure or arrangement that resembles a traditional dead end tower. It creates the impression of a termination point while allowing the line to carry on. It’s useful for maintaining line tension, future expansions, or changes in the grid layout. False dead ends also provide flexibility while ensuring the visual continuity of the line. It also conceals the fact that the line continues beyond that point. This is through using special hardware of configurations that allow the line to make a turn. False dead ends are from materials such as steel, aluminum, composite materials, and galvanized steel. They find use in straight sections, change in direction, transition points and maintenance access points on transmission lines. false dead ends also work to maintain the appearance of uniformity in the line.
Components of the false dead end
The false dead ends consist of several components working together to create a point that provides support and tension. This is while maintaining the appearance of a termination point to the transmission line. These components are able to withstand mechanical, electrical and environmental stresses. The available components vary depending on the design and needs of the project. The following are the components of the false dead end.
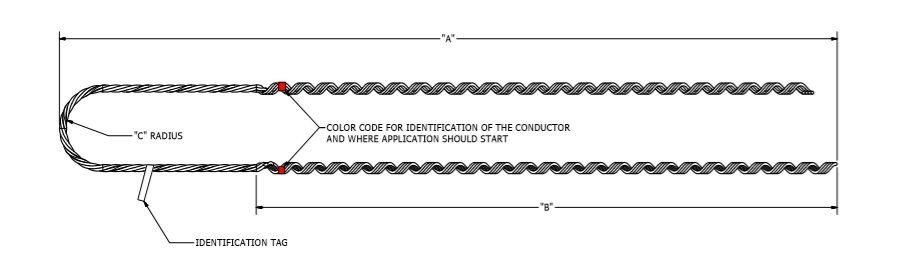
- Anchor structure – this is the support structure that anchors the transmission line. It is a strong framework attached to the ground.
- Tensioning hardware – this includes tensioners or tension clamps. They help to maintain the required tension in the transmission line. They also help to prevent sagging and ensure the proper alignment of the conductors.
- Insulators – these help to maintain the electrical insulation between the conductors and support structure. They help prevent the electrical current from flowing through the structure.
- Conductor attachment – these includes conductor clamps or connectors. They serve to attach the conductors to the support structure.
- Crossarms – these are horizontal members attached to the anchor structure supporting the conductors. They help distribute the weight of the conductors and maintain their spacing.
- Guy wires – these are tensioning cables that provide extra support to the anchor structure. They help to stabilize the cables and prevent swaying.
- Fasteners – these include components such as bolts, nuts, washers, and fasteners. They help to assemble the false dead end and secure its components together
Features of the false dead end
False dead ends consist of features that contribute to the functionality and aesthetic appeal. This allows for efficient and reliable operation while maintaining visual harmony with the surrounding landscape. The flowing are the common features of the false dead end.

- Appearance of termination – the dead ends have designs to appear as termination points. They give the impression that the line ends at that point.
- Structural support – false dead ends provide structural support to the transmission line. They also help to maintain tension and stability to ensure proper operation.
- Integration with surrounding – false dead ends have designs to blend into the surrounding landscape. This helps to maintain the visual continuity of the transmission line.
- Durability – the dead ends are from durable materials capable of withstanding environmental factors. The factors may include wind, weather, and temperature variations.
- Standardization – the dead ends may have standardized designs and features. These help to facilitate manufacturing and installation.
- Line continuation – the dead ends allow the transmission line to continue beyond the plain endpoint.
- Concealed hardware – hardware used in the construction of false dead ends is often concealed within the structure.
- Flexibility – the dead ends offer flexibility in the layout and design of the transmission line. This allows foe changes in direction, future expansion, or maintenance access. It does this without disrupting the appearance.
- Electrical insulation – insulating materials ensure electrical insulation between the conductors and the support structure. This helps to prevent leakage or electrical hazards.
Types of false dead ends
There are several types of false dead ends used in various applications. Each of these types serves specific purposes in different applications. This is including maintaining the functionality, stability and visual continuity. Additionally, it is important to select the right type of false dead end to suit your specific needs. The following are the common types of the false dead end.

- Straight line false dead end – this works in straight sections of the transmission lines. It works where the line appears to terminate but continues beyond the false dead end. It also provides support and tension to the line while maintaining a seamless appearance.
- Termination points false dead ends – false dead ends install at crucial termination points of the transmission line. It has designs to support the end of the line and maintain tension.
- Maintenance access false dead end – the dead ends may also install at specific intervals along the transmission line. It helps to provide access for maintenance activities. The dead ends incorporate features such as hinged components or removal sections to allow maintenance.
- Transition false dead end – transition false dead ends serve to mark the point of transition from overhead to ground. They provide support and tension while concealing the change in line configuration.
- Angle change false dead end – the dead ends serve as points where the transmission line changes direction. They provide support and tension while concealing the change in line configuration.
- Hybrid false dead end – some of the dead ends feature many types to meet specific designs. They also help to address unique challenges in the transmission line layout.
Materials used in the construction of the dead ends
Proper selection of false dead end materials helps to ensure their functionality and reliability. The choice depends on factors such as mechanical strength, electrical properties, environmental conditions and costs. Considering these factors helps to ensure the reliability, longevity and safety of the transmission line. Also, it is advisable to seek professional help when selecting from these materials. The following are the materials used in the manufacture of the false dead end.
- Steel – steel provides strength, durability, and ability to withstand high tension loads. Steel false dead ends provide the necessary support for the tension in the transmission line.
- Aluminum – this is lightweight ad corrosion resistant. It is suitable for components that need lighter construction while maintaining strength. It also offers good conductivity and corrosion resistance.
- Galvanized steel wire – this is suitable for tensioning the transmission line and providing support. This is due to its strength and resistance to corrosion.
- Composite materials – these include fiberglass or carbon fiber materials. they provide high strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance.
- Concrete – this works for the foundation or anchor structures of false dead ends. They help provide stability and support for the transmission line.
- Insulators – these help to maintain electrical insulation between the conductors and support structures. They are from materials such as porcelain, glass, or polymer composites.
Functions of false dead ends
False dead ends serve various functions in overhead transmission lines. They play a crucial role in functionality, safety and visual aesthetics of the lines. They also help to optimize their performance and integration into the surrounding. Also, it is advisable to understand the various functions before selection of the dead ends. The following are the common functions of the false dead ends.
- Visual continuity – false dead ends create the appearance of termination points in the transmission line. They maintain the visual continuity of the line while concealing its actual continuation.
- Structural support – the dead ends contribute to the structural integrity of the transmission lines. It anchors it securely to the ground and supports the weight of the conductors.
- Maintenance access – they incorporate features such as hinged components or removable sections. They help provide access for maintenance activities, facilitating inspection, repair or replacement of components.
- Aesthetic enhancement – they contribute to the aesthetic appeal of overhead transmission lines. They reduce the impact on the surrounding landscape or environment by reducing visual clutter.
- Tension maintenance – they provide support and tension to the transmission line. This helps to prevent sagging and ensuring the conductors remain at the desired height and alignment.
- Flexibility in design – they allow flexibility in the design and layout of the transmission line. It also helps accommodate changes in direction, elevation, or configuration.
- Safety – false dead ends ensure the safety of the line by reducing the risk of structural failure of damage.
- Line direction changes concealment – false dead ends help conceal the changes and maintain the appearance of a continuous line. This is while allowing for efficient transmission of electricity.
Frequently asked questions
A false dead end is a component that creates the appearance of a termination point in an overhead transmission line. It does this while allowing the line to continue beyond that point.
False dead ends help to maintain the visual continuity of the transmission lines and provide support. They also accommodate changes in direction, ease maintenance access and enhance the aesthetics.
False dead ends provide visual continuity, tension maintenance, structural support and flexibility in design.
